Marked HDL deficiency and premature coronary heart disease
- PMID: 20616715
- PMCID: PMC6942922
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32833c1ef6
Marked HDL deficiency and premature coronary heart disease
Abstract
Purpose of review: Our purpose is to review recent publications in the area of marked human HDL deficiency, HDL particles, coronary heart disease (CHD), amyloidosis, the immune response, and kidney disease.
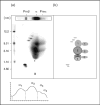
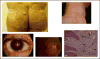
Recent findings: Lack of detectable plasma apolipoprotein (apo) A-I can be due to DNA deletions, rearrangements, or nonsense or frameshift mutations within the APOA1 gene resulting in a lack of apoA-I secretion. Such patients have marked HDL deficiency, normal levels of triglycerides and LDL cholesterol, and can have xanthomas and premature CHD. ApoA-I variants with amino acid substitutions, especially in the region of amino acid residues 50-93 and 170-178, have been associated with amyloidosis. Patients with homozygous Tangier disease have defective cellular cholesterol efflux due to mutations in the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter A1, detectable plasma apoA-I levels and prebeta-1 HDL in their plasma. They have decreased LDL cholesterol levels and can develop neuropathy and premature CHD. Patients with lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency have both prebeta-1 and alpha-4 HDL present in their plasma and develop corneal opacities, anemia, proteinuria, and kidney failure.
Summary: Patients with marked HDL deficiency can have great differences in their clinical phenotype depending on the underlying defect.
Figures





Similar articles
-
High-density lipoprotein metabolism, composition, function, and deficiency.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014 Jun;25(3):194-9. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000074. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014. PMID: 24785961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High density lipoprotein deficiency with xanthomas. A defect in reverse cholesterol transport caused by a point mutation in the apolipoprotein A-I gene.J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2262-73. doi: 10.1172/JCI116830. J Clin Invest. 1993. PMID: 7693760 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally occurring and bioengineered apoA-I mutations that inhibit the conversion of discoidal to spherical HDL: the abnormal HDL phenotypes can be corrected by treatment with LCAT.Biochem J. 2007 Aug 15;406(1):167-74. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070296. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17506726 Free PMC article.
-
LCAT can rescue the abnormal phenotype produced by the natural ApoA-I mutations (Leu141Arg)Pisa and (Leu159Arg)FIN.Biochemistry. 2007 Sep 18;46(37):10713-21. doi: 10.1021/bi7003203. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17711302
-
Genetic determinants of low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004 Jul;19(4):380-4. doi: 10.1097/01.hco.0000126584.12520.b5. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15218400 Review.
Cited by
-
Time-resolved fluorescence based direct two-site apoA-I immunoassays and their clinical application in patients with suspected obstructive coronary artery disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 14;9:912578. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.912578. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36312264 Free PMC article.
-
HDL cholesterol: reappraisal of its clinical relevance.Clin Res Cardiol. 2017 Sep;106(9):663-675. doi: 10.1007/s00392-017-1106-1. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Clin Res Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28342064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dyslipidemia and diabetes: reciprocal impact of impaired lipid metabolism and Beta-cell dysfunction on micro- and macrovascular complications.Rev Diabet Stud. 2012 Summer-Fall;9(2-3):82-93. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2012.9.82. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Rev Diabet Stud. 2012. PMID: 23403704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of SCP-2/SCP-x gene ablation and dietary cholesterol on hepatic lipid accumulation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Sep 1;309(5):G387-99. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00460.2014. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26113298 Free PMC article.
-
A decreased level of high-density lipoprotein is a possible risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 20;6(12):e1779. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1779. eCollection 2023 Dec. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38125279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Santos RD, Schaefer EJ, Asztalos BF, et al. Characterization of high density lipoprotein particles in familial apolipoprotein A-I deficiency. J Lipid Res. 2008;46:349–357. - PubMed
-
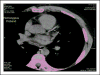
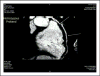
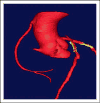
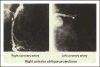
- Santos RD, Miname MH, Martinez LR, et al. Noninvasive detection of aortic and coronary atherosclerosis in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia by 64 slice multidetector row computed tomography angiography. Atherosclerosis. 2008;197:910–915. - PubMed
-
- Wada M, Iso T, Asztalos BF, et al. Marked high density lipoprotein deficiency due to apolipoprotein A-I Tomioka (codon 138 deletion) Atherosclerosis. 2009;207:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Favari E, Calabresi L, Adorni MP, et al. Small discoidal prebeta1 HDL particles are efficient acceptors of cell cholesterol via ABCA1 and ABCG1. Biochemistry. 2009;48:11067–11074. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

