Overexpression of the wild-type SPT1 subunit lowers desoxysphingolipid levels and rescues the phenotype of HSAN1
- PMID: 19923297
- PMCID: PMC3849752
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2536-09.2009
Overexpression of the wild-type SPT1 subunit lowers desoxysphingolipid levels and rescues the phenotype of HSAN1
Abstract
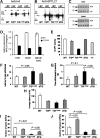
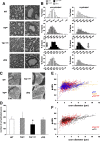
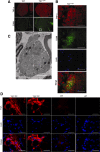
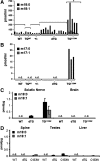
Mutations in the SPTLC1 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) cause an adult-onset, hereditary sensory, and autonomic neuropathy type I (HSAN1). We previously reported that mice bearing a transgene-expressing mutant SPTLC1 (tgSPTLC1(C133W)) show a reduction in SPT activity and hyperpathia at 10 months of age. Now analyzed at a later age, we find these mice develop sensory loss with a distal small fiber neuropathy and peripheral myelinopathy. This phenotype is largely reversed when these mice are crossed with transgenic mice overexpressing wild-type SPTLC1 showing that the mutant SPTLC1 protein is not inherently toxic. Simple loss of SPT activity also cannot account for the HSAN1 phenotype, since heterozygous SPTLC1 knock-out mice have reduced SPT activity but are otherwise normal. Rather, the presence of two newly identified, potentially deleterious deoxysphingoid bases in the tgSPTLC1(C133W), but not in the wild-type, double-transgenic tgSPTLC1(WT + C133W) or SPTLC1(+/-) mice, suggests that the HSAN1 mutations alter amino acid selectivity of the SPT enzyme such that palmitate is condensed with alanine and glycine, in addition to serine. This observation is consistent with the hypothesis that HSAN1 is the result of a gain-of-function mutation in SPTLC1 that leads to accumulation of a toxic metabolite.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral L-serine supplementation reduces production of neurotoxic deoxysphingolipids in mice and humans with hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type 1.J Clin Invest. 2011 Dec;121(12):4735-45. doi: 10.1172/JCI57549. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 22045570 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mutant SPTLC1 dominantly inhibits serine palmitoyltransferase activity in vivo and confers an age-dependent neuropathy.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Nov 15;14(22):3507-21. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi380. Epub 2005 Oct 6. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 16210380
-
HSAN1 mutations in serine palmitoyltransferase reveal a close structure-function-phenotype relationship.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Mar 1;25(5):853-65. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv611. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 26681808
-
Serine Palmitoyltransferase (SPT)-related Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Disorders.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024;11(4):735-747. doi: 10.3233/JND-240014. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024. PMID: 38788085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Jun 10;1632(1-3):16-30. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(03)00059-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12782147 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-dependent small fiber neuropathy: Mechanistic insights from animal models.Exp Neurol. 2024 Jul;377:114811. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114811. Epub 2024 May 7. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38723859 Review.
-
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 (HSANI) caused by a novel mutation in SPTLC2.Neurology. 2013 Jun 4;80(23):2106-11. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318295d789. Epub 2013 May 8. Neurology. 2013. PMID: 23658386 Free PMC article.
-
Regression of schwannomas induced by adeno-associated virus-mediated delivery of caspase-1.Hum Gene Ther. 2013 Feb;24(2):152-62. doi: 10.1089/hum.2012.094. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Hum Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23140466 Free PMC article.
-
A Model of Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathy Type 1 Reveals a Role of Glycosphingolipids in Neuronal Polarity.J Neurosci. 2019 Jul 17;39(29):5816-5834. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2541-18.2019. Epub 2019 May 28. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31138658 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 is caused by the accumulation of two neurotoxic sphingolipids.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 9;285(15):11178-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092973. Epub 2010 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20097765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auer-Grumbach M, De Jonghe P, Verhoeven K, Timmerman V, Wagner K, Hartung HP, Nicholson GA. Autosomal dominant inherited neuropathies with prominent sensory loss and mutilations: a review. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:329–334. - PubMed
-
- Bejaoui K, Wu C, Scheffler MD, Haan G, Ashby P, Wu L, de Jong P, Brown RH., Jr SPTLC1 is mutated in hereditary sensory neuropathy, type 1. Nat Genet. 2001;27:261–262. - PubMed
-
- Broom DC, Samad TA, Kohno T, Tegeder I, Geisslinger G, Woolf CJ. Cyclooxygenase 2 expression in the spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience. 2004;124:891–900. - PubMed
-
- Dedov VN, Dedova IV, Merrill AH, Jr, Nicholson GA. Activity of partially inhibited serine palmitoyltransferase is sufficient for normal sphingolipid metabolism and viability of HSN1 patient cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1688:168–175. - PubMed
-
- Hanada K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1632:16–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
