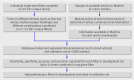
Filtering Medline for a clinical discipline: diagnostic test assessment framework
- PMID: 19767336
- PMCID: PMC2746885
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.b3435
Filtering Medline for a clinical discipline: diagnostic test assessment framework
Abstract
Objective: To develop and test a Medline filter that allows clinicians to search for articles within a clinical discipline, rather than searching the entire Medline database.
Design: Diagnostic test assessment framework with development and validation phases.
Setting: Sample of 4657 articles published in 2006 from 40 journals. Reviews Each article was manually reviewed, and 19.8% contained information relevant to the discipline of nephrology. The performance of 1 155 087 unique renal filters was compared with the manual review.
Main outcome measures: Sensitivity, specificity, precision, and accuracy of each filter.
Results: The best renal filters combined two to 14 terms or phrases and included the terms "kidney" with multiple endings (that is, truncation), "renal replacement therapy", "renal dialysis", "kidney function tests", "renal", "nephr" truncated, "glomerul" truncated, and "proteinuria". These filters achieved peak sensitivities of 97.8% and specificities of 98.5%. Performance of filters remained excellent in the validation phase.
Conclusions: Medline can be filtered for the discipline of nephrology in a reliable manner. Storing these high performance renal filters in PubMed could help clinicians with their everyday searching. Filters can also be developed for other clinical disciplines by using similar methods.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dialysis search filters for PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Embase databases.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Oct;7(10):1624-31. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02360312. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22917701 Free PMC article.
-
Glomerular disease search filters for Pubmed, Ovid Medline, and Embase: a development and validation study.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012 Jun 6;12:49. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-12-49. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012. PMID: 22672435 Free PMC article.
-
Search strategies to identify diagnostic accuracy studies in MEDLINE and EMBASE.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 11;2013(9):MR000022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000022.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24022476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-performance information search filters for CKD content in PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and EMBASE.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Jan;65(1):26-32. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25059221
-
High-performance information search filters for acute kidney injury content in PubMed, Ovid Medline and Embase.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014 Apr;29(4):823-32. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft531. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24449104 Review.
Cited by
-
A search strategy to identify studies on the prognosis of work disability: a diagnostic test framework.BMJ Open. 2015 May 19;5(5):e006315. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006315. BMJ Open. 2015. PMID: 25991444 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity and predictive value of 15 PubMed search strategies to answer clinical questions rated against full systematic reviews.J Med Internet Res. 2012 Jun 12;14(3):e85. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2021. J Med Internet Res. 2012. PMID: 22693047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validity of physician billing claims to identify deceased organ donors in large healthcare databases.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 14;8(8):e70825. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070825. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967114 Free PMC article.
-
Dialysis search filters for PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Embase databases.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Oct;7(10):1624-31. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02360312. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22917701 Free PMC article.
-
Glomerular disease search filters for Pubmed, Ovid Medline, and Embase: a development and validation study.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012 Jun 6;12:49. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-12-49. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012. PMID: 22672435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Library of Medicine. Key Medline indicators. 2008. www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/bsd_key.html. - PubMed
-
- NLM Systems Data News and Update Information. 2009. www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/revup/revup_pub.html.
-
- National Library of Medicine. Number of titles currently indexed for Index Medicus and Medline on PubMed. 2009. www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/num_titles.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources