Mutations in 3 genes (MKS3, CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L) cause COACH syndrome (Joubert syndrome with congenital hepatic fibrosis)
- PMID: 19574260
- PMCID: PMC3501959
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2009.067249
Mutations in 3 genes (MKS3, CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L) cause COACH syndrome (Joubert syndrome with congenital hepatic fibrosis)
Abstract
Objective: To identify genetic causes of COACH syndrome
Background: COACH syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterised by Cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, Oligophrenia (developmental delay/mental retardation), Ataxia, Coloboma, and Hepatic fibrosis. The vermis hypoplasia falls in a spectrum of mid-hindbrain malformation called the molar tooth sign (MTS), making COACH a Joubert syndrome related disorder (JSRD).
Methods: In a cohort of 251 families with JSRD, 26 subjects in 23 families met criteria for COACH syndrome, defined as JSRD plus clinically apparent liver disease. Diagnostic criteria for JSRD were clinical findings (intellectual impairment, hypotonia, ataxia) plus supportive brain imaging findings (MTS or cerebellar vermis hypoplasia). MKS3/TMEM67 was sequenced in all subjects for whom DNA was available. In COACH subjects without MKS3 mutations, CC2D2A, RPGRIP1L and CEP290 were also sequenced.
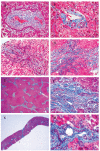
Results: 19/23 families (83%) with COACH syndrome carried MKS3 mutations, compared to 2/209 (1%) with JSRD but no liver disease. Two other families with COACH carried CC2D2A mutations, one family carried RPGRIP1L mutations, and one lacked mutations in MKS3, CC2D2A, RPGRIP1L and CEP290. Liver biopsies from three subjects, each with mutations in one of the three genes, revealed changes within the congenital hepatic fibrosis/ductal plate malformation spectrum. In JSRD with and without liver disease, MKS3 mutations account for 21/232 families (9%).
Conclusions: Mutations in MKS3 are responsible for the majority of COACH syndrome, with minor contributions from CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L; therefore, MKS3 should be the first gene tested in patients with JSRD plus liver disease and/or coloboma, followed by CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suspected Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease but Cerebellar Vermis Hypoplasia, Oligophrenia Ataxia, Coloboma, and Hepatic Fibrosis (COACH) Syndrome in Retrospect, A Delayed Diagnosis Aided by Genotyping and Reverse Phenotyping: A Case Report and A Review of the Literature.Nephron. 2024;148(4):264-272. doi: 10.1159/000527991. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Nephron. 2024. PMID: 36617405 Review.
-
MKS3/TMEM67 mutations are a major cause of COACH Syndrome, a Joubert Syndrome related disorder with liver involvement.Hum Mutat. 2009 Feb;30(2):E432-42. doi: 10.1002/humu.20924. Hum Mutat. 2009. PMID: 19058225 Free PMC article.
-
CC2D2A is mutated in Joubert syndrome and interacts with the ciliopathy-associated basal body protein CEP290.Am J Hum Genet. 2008 Nov;83(5):559-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.10.002. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Am J Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18950740 Free PMC article.
-
Functional validation of novel MKS3/TMEM67 mutations in COACH syndrome.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 31;7(1):10222. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10652-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28860541 Free PMC article.
-
Joubert syndrome and related disorders.Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2012 Jul-Aug;46(4):379-83. doi: 10.5114/ninp.2012.30457. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2012. PMID: 23023437 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of Ocular Manifestations of Joubert Syndrome.Genes (Basel). 2018 Dec 4;9(12):605. doi: 10.3390/genes9120605. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30518138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and molecular features of Joubert syndrome and related disorders.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2009 Nov 15;151C(4):326-40. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30229. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 19876931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joubert Syndrome: Ophthalmological Findings in Correlation with Genotype and Hepatorenal Disease in 99 Patients Prospectively Evaluated at a Single Center.Ophthalmology. 2018 Dec;125(12):1937-1952. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.05.026. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Ophthalmology. 2018. PMID: 30055837 Free PMC article.
-
Joubert syndrome: a model for untangling recessive disorders with extreme genetic heterogeneity.J Med Genet. 2015 Aug;52(8):514-22. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103087. Epub 2015 Jun 19. J Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 26092869 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype-phenotype correlates in Joubert syndrome: A review.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022 Mar;190(1):72-88. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31963. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 35238134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verloes A, Lambotte C. Further delineation of a syndrome of cerebellar vermis hypo/aplasia, oligophrenia, congenital ataxia, coloboma, and hepatic fibrosis. Am J Med Genet. 1989;32:227–32. - PubMed
-
- Satran D, Pierpont ME, Dobyns WB. Cerebello-oculo-renal syndromes including Arima, Senior-Loken and COACH syndromes: more than just variants of Joubert syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1999;86:459–69. - PubMed
-
- Gleeson JG, Keeler LC, Parisi MA, Marsh SE, Chance PF, Glass IA, Graham JM, Jr, Maria BL, Barkovich AJ, Dobyns WB. Molar tooth sign of the midbrain-hindbrain junction: occurrence in multiple distinct syndromes. Am J Med Genet. 2004;125A:25–34. discussion 17. - PubMed
-
- Maria BL, Quisling RG, Rosainz LC, Yachnis AT, Gitten JC, Dede DE, Fennell E. Molar tooth sign in Joubert syndrome: clinical, radiologic, and pathologic significance. J Child Neurol. 1999;14:368–76. - PubMed
-
- Saraiva JM, Baraitser M. Joubert syndrome: a review. Am J Med Genet. 1992;43:726–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K24HD46712/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 HG999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000423/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 5KL2RR025015/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 MH999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025015/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 HL999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS050375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS045832/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HD046712/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS064077/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025015-03/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23NS45832/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
