Dysregulation of the C/EBPalpha differentiation pathway in human cancer
- PMID: 19075268
- PMCID: PMC2645860
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.9812
Dysregulation of the C/EBPalpha differentiation pathway in human cancer
Abstract
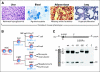
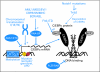
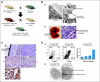
While much is known about aberrant pathways affecting cell growth and apoptosis, our understanding of another critical step of neoplastic transformation, differentiation arrest, remains poor. The differentiation-inducing transcription factor CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) is required for proper control of adipogenesis, glucose metabolism, granulocytic differentiation, and lung development. Studies investigating the function of this protein in hematopoietic malignancies as well as in lung and skin cancer have revealed numerous ways how tumor cells abrogate C/EBPalpha function. Genetic and global expression analysis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases identifies C/EBPalpha-deficient AML as a separate entity yielding novel classification schemes. In patients with a dysfunctional C/EBPalpha pathway, targeted therapies may overcome the block in differentiation, and in combination with conventional chemotherapy, may lead to complete eradication of the malignant clone. Overall, a better understanding of the mechanisms of how C/EBPalpha dysregulation participates in the neoplastic process has opened new gateways for differentiation biology research.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of C/EBPalpha activity alters gene expression and differentiation of human CD34+ cells.Blood. 2003 Mar 15;101(6):2206-14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-05-1546. Epub 2002 Oct 24. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12406909
-
Genetic ablation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha in epidermis reveals its role in suppression of epithelial tumorigenesis.Cancer Res. 2007 Jul 15;67(14):6768-76. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0139. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17638888 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPα dysregulation in AML and ALL.Crit Rev Oncog. 2011;16(1-2):93-102. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i1-2.90. Crit Rev Oncog. 2011. PMID: 22150310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Absence of the transcription factor CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha results in loss of myeloid identity in bcr/abl-induced malignancy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Apr 18;103(16):6338-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508143103. Epub 2006 Apr 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16606850 Free PMC article.
-
C/EBPα deregulation as a paradigm for leukemogenesis.Leukemia. 2017 Nov;31(11):2279-2285. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.229. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 28720765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of PI3K and Hippo signaling pathways synergistically induces chronic pancreatitis via CTGF upregulation.J Clin Invest. 2021 Jul 1;131(13):e143414. doi: 10.1172/JCI143414. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34032634 Free PMC article.
-
Functional inhibition of MEF2 by C/EBP is a possible mechanism of leukemia development by CEBP-IGH fusion gene.Cancer Sci. 2023 Mar;114(3):781-792. doi: 10.1111/cas.15641. Epub 2022 Nov 27. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36341510 Free PMC article.
-
Deoxynivalenol Exposure Suppresses Adipogenesis by Inhibiting the Expression of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma 2 (PPARγ2) in 3T3-L1 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6300. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176300. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32878272 Free PMC article.
-
Trib2 Suppresses Tumor Initiation in Notch-Driven T-ALL.PLoS One. 2016 May 18;11(5):e0155408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155408. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27191957 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoiesis in the equine fetal liver suggests immune preparedness.Immunogenetics. 2014 Nov;66(11):635-49. doi: 10.1007/s00251-014-0799-9. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Immunogenetics. 2014. PMID: 25179685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tenen DG, Hromas R, Licht JD, et al. Transcription factors, normal myeloid development, and leukemia. Blood. 1997;90:489–519. - PubMed
-
- Pabst T, Mueller BU, Zhang P, et al. Dominant-negative mutations of C/EBPα, encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha (C/EBP alpha), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2001;27:263–270. - PubMed
-
- Tenen DG. Disruption of differentiation in human cancer: AML shows the way. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:89–101. - PubMed
-
- Landschulz WH, Johnson PF, Adashi EY, et al. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988;2:786–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

