Mutations in the nervous system--specific HSN2 exon of WNK1 cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type II
- PMID: 18521183
- PMCID: PMC2398735
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI34088
Mutations in the nervous system--specific HSN2 exon of WNK1 cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type II
Abstract
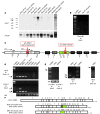
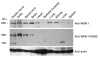
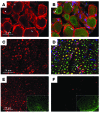
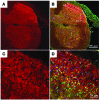
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type II (HSANII) is an early-onset autosomal recessive disorder characterized by loss of perception to pain, touch, and heat due to a loss of peripheral sensory nerves. Mutations in hereditary sensory neuropathy type II (HSN2), a single-exon ORF originally identified in affected families in Quebec and Newfoundland, Canada, were found to cause HSANII. We report here that HSN2 is a nervous system-specific exon of the with-no-lysine(K)-1 (WNK1) gene. WNK1 mutations have previously been reported to cause pseudohypoaldosteronism type II but have not been studied in the nervous system. Given the high degree of conservation of WNK1 between mice and humans, we characterized the structure and expression patterns of this isoform in mice. Immunodetections indicated that this Wnk1/Hsn2 isoform was expressed in sensory components of the peripheral nervous system and CNS associated with relaying sensory and nociceptive signals, including satellite cells, Schwann cells, and sensory neurons. We also demonstrate that the novel protein product of Wnk1/Hsn2 was more abundant in sensory neurons than motor neurons. The characteristics of WNK1/HSN2 point to a possible role for this gene in the peripheral sensory perception deficits characterizing HSANII.
Figures


Similar articles
-
WNK1/HSN2 mutation in human peripheral neuropathy deregulates KCC2 expression and posterior lateral line development in zebrafish (Danio rerio).PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003124. Epub 2013 Jan 3. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23300475 Free PMC article.
-
Expression pattern analysis and characterization of the hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy 2 A (HSAN2A) gene with no lysine kinase (WNK1) in human dorsal root ganglion.Exp Neurol. 2023 Dec;370:114552. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114552. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37793538
-
KIF1A, an axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles, is mutated in hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2.Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Aug 12;89(2):219-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.06.013. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Am J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21820098 Free PMC article.
-
The WNKs: atypical protein kinases with pleiotropic actions.Physiol Rev. 2011 Jan;91(1):177-219. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00017.2010. Physiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21248166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular genetics of hereditary sensory neuropathies.Neuromolecular Med. 2006;8(1-2):147-58. doi: 10.1385/nmm:8:1-2:147. Neuromolecular Med. 2006. PMID: 16775373 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes through Integrated Study of Alzheimer's Disease Affected Brain Regions.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 6;11(4):e0152342. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152342. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27050411 Free PMC article.
-
With no lysine L-WNK1 isoforms are negative regulators of the K+-Cl- cotransporters.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):C54-66. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00193.2015. Epub 2016 May 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27170636 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide gene expression profiling of human narcolepsy.Gene Expr. 2012;15(4):171-81. doi: 10.3727/105221612x13372578119652. Gene Expr. 2012. PMID: 22783726 Free PMC article.
-
WNK2 kinase is a novel regulator of essential neuronal cation-chloride cotransporters.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 26;286(34):30171-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.222893. Epub 2011 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21733846 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Processes Modulated by the Chloride-Sensitive WNK-SPAK/OSR1 Kinase Signaling Pathway and the Cation-Coupled Chloride Cotransporters.Front Physiol. 2020 Oct 20;11:585907. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.585907. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33192599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verhoeven K., et al. Recent advances in hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006;19:474–480. - PubMed
-
- Kondo K., Horikawa Y. Genetic heterogeneity of hereditary sensory neuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 1974;30:336–337. - PubMed
-
- Ota M., Ellefson R.D., Lambert E.H., Dyck P.J. Hereditary sensory neuropathy, type II. Clinical, electrophysiologic, histologic, and biochemical studies of a Quebec kinship. Arch. Neurol. 1973;29:23–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

