Inhibition of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 degradation of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein by alpha-2-macroglobulin
- PMID: 18485748
- PMCID: PMC2574789
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2008.03.017
Inhibition of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 degradation of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein by alpha-2-macroglobulin
Abstract
Objective: As we previously reported, ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12, two members of ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin motifs) family, degrade cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) in vitro and are significantly induced in the cartilage and synovium of arthritic patients [Liu CJ, Kong W, Ilalov K, Yu S, Xu K, Prazak L, et al. ADAMTS-7: a metalloproteinase that directly binds to and degrades cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. FASEB J 2006;20(7):988-90; Liu CJ, Kong W, Xu K, Luan Y, Ilalov K, Sehgal B, et al. ADAMTS-12 associates with and degrades cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. J Biol Chem 2006;281(23):15800-8]. The purpose of this study was to determine (1) whether cleavage activity of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 of COMP are associated with COMP degradation in osteoarthritis (OA); (2) whether alpha-2-macroglobulin (a(2)M) is a novel substrate for ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12; and (3) whether a(2)M inhibits ADAMTS-7 or ADAMTS-12 cleavage of COMP.
Methods: An in vitro digestion assay was used to examine the degradation of COMP by ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 in the cartilage of OA patients; in cartilage explants incubated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or interleukin-1-beta (IL-1beta) with or without blocking antibodies; and in human chondrocytes treated with specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) to knockdown ADAMTS-7 or/and ADAMTS-12. Digestion of a(2)M by ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 in vitro and the inhibition of ADAMTS-7 or ADAMTS-12-mediated digestion of COMP by a(2)M were also analyzed.
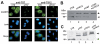
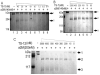
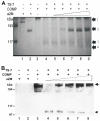
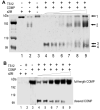
Results: The molecular mass of the COMP fragments produced by either ADAMTS-7 or ADAMTS-12 were similar to those observed in OA patients. Specific blocking antibodies against ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 dramatically inhibited TNF-alpha- or IL-1beta-induced COMP degradation in the cultured cartilage explants. The suppression of ADAMTS-7 or ADAMTS-12 expression by siRNA silencing in the human chondrocytes also prevented TNF-alpha- or IL-1beta-induced COMP degradation. Both ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 were able to cleave a(2)M, giving rise to 180- and 105-kDa cleavage products, respectively. Furthermore, a(2)M inhibited both ADAMTS-7- and ADAMTS-12-mediated COMP degradation in a concentration (or dose)-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Our observations demonstrate the importance of COMP degradation by ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 in vivo. Furthermore, a(2)M is a novel substrate for ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12. More significantly, a(2)M represents the first endogenous inhibitor of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 in the pathogenesis of arthritis.Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009 Jan;5(1):38-45. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0961. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19098927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Granulin-epithelin precursor binds directly to ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 and inhibits their degradation of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Jul;62(7):2023-36. doi: 10.1002/art.27491. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20506400 Free PMC article.
-
ADAMTS-12 associates with and degrades cartilage oligomeric matrix protein.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 9;281(23):15800-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513433200. Epub 2006 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16611630 Free PMC article.
-
ADAMTS-7: a metalloproteinase that directly binds to and degrades cartilage oligomeric matrix protein.FASEB J. 2006 May;20(7):988-90. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-3877fje. Epub 2006 Apr 3. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16585064 Free PMC article.
-
ADAMTS-7, a novel proteolytic culprit in vascular remodeling.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2010 Aug 25;62(4):285-94. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 20717629 Review.
Cited by
-
Omics Profiling of S2P Mutant Fibroblasts as a Mean to Unravel the Pathomechanism and Molecular Signatures of X-Linked MBTPS2 Osteogenesis Imperfecta.Front Genet. 2021 May 21;12:662751. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.662751. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34093655 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging roles of ADAMTS-7 and ADAMTS-12 matrix metalloproteinases.Open Access Rheumatol. 2009 Sep 22;1:121-131. doi: 10.2147/oarrr.s6264. eCollection 2009. Open Access Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 27789986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of ADAMTSs in arthritis.Protein Cell. 2010 Jan;1(1):33-47. doi: 10.1007/s13238-010-0002-5. Epub 2010 Feb 7. Protein Cell. 2010. PMID: 21203996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17A enhances ADAMTS-7 expression through regulation of TNF-α in human nucleus pulposus cells.J Mol Histol. 2015 Dec;46(6):475-83. doi: 10.1007/s10735-015-9640-5. Epub 2015 Oct 7. J Mol Histol. 2015. PMID: 26446668
-
New insights into the pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis: microarray analysis of gene expression in a rat model.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(3):R124. doi: 10.1186/ar3062. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20579363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salzet M. Leech thrombin inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des. 2002;8(7):493–503. - PubMed
-
- DiCesare P, Hauser N, Lehman D, Pasumarti S, Paulsson M. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) is an abundant component of tendon. FEBS Lett. 1994;354(2):237–240. - PubMed
-
- Hedbom E, Antonsson P, Hjerpe A, Aeschlimann D, Paulsson M, Rosa-Pimentel E, et al. Cartilage matrix proteins. An acidic oligomeric protein (COMP) detected only in cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(9):6132–6136. - PubMed
-
- Morgelin M, Engel J, Heinegard D, Paulsson M. Proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. Structure of the aggregates extracted with associative and dissociative solvents as revealed by electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(20):14275–14284. - PubMed
-
- Oldberg A, Antonsson P, Lindblom K, Heinegard D. COMP (cartilage oligomeric matrix protein) is structurally related to the thrombospondins. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(31):22346–22350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03 AR052022-03/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR052676-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR053210/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR052022-01A1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR052022-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR053210-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR053210-01A2/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR052022/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR052676-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR052676/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR052022-01A1S1/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG029388/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022021-08/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022021/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR053210/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG029388-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR052022/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG029388/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG029388-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR050620/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

