KBG syndrome
- PMID: 17163996
- PMCID: PMC1764006
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-1-50
KBG syndrome
Abstract
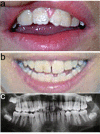
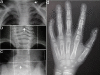
KBG syndrome is a rare condition characterised by a typical facial dysmorphism, macrodontia of the upper central incisors, skeletal (mainly costovertebral) anomalies and developmental delay. To date, KBG syndrome has been reported in 45 patients. Clinical features observed in more than half of patients that may support the diagnosis are short stature, electroencephalogram (EEG) anomalies (with or without seizures) and abnormal hair implantation. Cutaneous syndactyly, webbed short neck, cryptorchidism, hearing loss, palatal defects, strabismus and congenital heart defects are less common findings. Autosomal dominant transmission has been observed in some families, and it is predominantly the mother, often showing a milder clinical picture, that transmits the disease. The diagnosis is currently based solely on clinical findings as the aetiology is unknown. The final diagnosis is generally achieved after the eruption of upper permanent central incisors at 7-8 years of age when the management of possible congenital anomalies should have been already planned. A full developmental assessment should be done at diagnosis and, if delays are noted, an infant stimulation program should be initiated. Subsequent management and follow-up should include an EEG, complete orthodontic evaluation, skeletal investigation with particular regard to spine curvatures and limb asymmetry, hearing testing and ophthalmologic assessment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
KBG syndrome: review of the literature and findings of 5 affected patients.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009 Sep;108(3):e72-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.04.035. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009. PMID: 19716495 Review.
-
Solitary median maxillary central incisor (SMMCI) syndrome.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006 Apr 9;1:12. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-1-12. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006. PMID: 16722608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The KBG syndrome-a syndrome of short stature, characteristic facies, mental retardation, macrodontia and skeletal anomalies.Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(5):7-18. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975. PMID: 1218237 No abstract available.
-
Six additional cases of the KBG syndrome: clinical reports and outline of the diagnostic criteria.Am J Med Genet. 1994 Sep 1;52(3):302-7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320520310. Am J Med Genet. 1994. PMID: 7810561
-
Further delineation of deletion 1p36 syndrome in 60 patients: a recognizable phenotype and common cause of developmental delay and mental retardation.Pediatrics. 2008 Feb;121(2):404-10. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-0929. Pediatrics. 2008. PMID: 18245432
Cited by
-
ANKRD11 variants cause variable clinical features associated with KBG syndrome and Coffin-Siris-like syndrome.J Hum Genet. 2017 Aug;62(8):741-746. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2017.24. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28250421 Free PMC article.
-
The KBG syndrome: Case report.Cases J. 2008 Sep 26;1(1):186. doi: 10.1186/1757-1626-1-186. Cases J. 2008. PMID: 18822138 Free PMC article.
-
A de novo microdeletion of ANKRD11 gene in a Korean patient with KBG syndrome.Ann Lab Med. 2014 Sep;34(5):390-4. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.5.390. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Ann Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 25187894 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of ANKRD11 mutations in humans and mice related to KBG syndrome.Hum Genet. 2015 Feb;134(2):181-90. doi: 10.1007/s00439-014-1509-2. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25413698 Clinical Trial.
-
DYSMORPHIC features and adult short stature: possible clinical markers of KBG syndrome.Ital J Pediatr. 2021 Jan 25;47(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13052-021-00961-5. Ital J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33494799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herrmann J, Pallister PD, Tiddy W, Opitz JM. The KBG syndrome-a syndrome of short stature, characteristic facies, mental retardation, macrodontia and skeletal anomalies. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Devriendt K, Holvoet M, Fryns JP. Further delineation of the KBG syndrome. Genet Couns. 1998;9:191–194. - PubMed
-
- Fryns JP, Haspeslagh M. Mental retardation, short stature, minor skeletal anomalies, craniofacial dysmorphism and macrodontia in two sisters and their mother. Another variant example of the KBG syndrome? Clin Genet. 1984;26:69–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

