Rapid determination of reduced and oxidized glutathione levels using a new thiol-masking reagent and the enzymatic recycling method: application to the rat liver and bile samples
- PMID: 16547740
- PMCID: PMC1483140
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-006-0375-8
Rapid determination of reduced and oxidized glutathione levels using a new thiol-masking reagent and the enzymatic recycling method: application to the rat liver and bile samples
Abstract
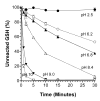
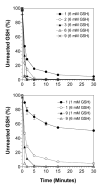
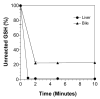
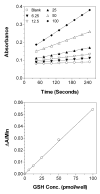
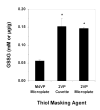
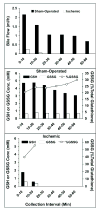
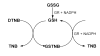
A microtiter plate assay for quantitation of reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) glutathione in the rat liver tissue and bile is described. The assay is based on the established enzymatic recycling method and a new thiol-masking reagent, 1-methyl-4-vinyl-pyridinium trifluoromethane sulfonate (M4VP). Samples were first processed by homogenization with (liver) or addition of (bile) sulfosalicylic acid. The total glutathione and GSSG were then determined before and after rapid (< or = 2 min) and efficient (100%) masking of the GSH content of the samples with M4VP followed by the enzymatic recycling assay. The percentages of error and coefficient of variation of the assay were within the accepted guidelines, indicating the accuracy and precision of the assay in the range of 6.25-100 pmol GSH per microplate well and 2.17-140 pmol GSSG per well, with lower limit of quantitation of 6.25 and 2.17 pmol per well for GSH and GSSG, respectively. Furthermore, the recoveries of added GSH or GSSG from the liver and bile samples were accurate and precise. The assay was applied to measurement of GSH, GSSG, and GSH:GSSG ratio in the liver and serially collected bile samples in sham-operated and ischemic rat livers, demonstrating a depletion of glutathione and a decrease in the GSH:GSSG ratio as a result of ischemia. The developed assay is rapid, sensitive, accurate, and precise and is suitable for studies of the redox status of liver under physiologic and pathophysiologic conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validated high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical method for determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in small tissue samples.Anal Biochem. 1997 Apr 5;247(1):63-8. doi: 10.1006/abio.1997.2032. Anal Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9126372
-
Biliary excretion of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in the rat. Regulation and response to oxidative stress.J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):124-33. doi: 10.1172/JCI111182. J Clin Invest. 1984. PMID: 6690473 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in biliary glutathione level during ischemia-reperfusion of rat liver.J Surg Res. 1994 Nov;57(5):569-73. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1994.1184. J Surg Res. 1994. PMID: 7967594
-
Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method.Nat Protoc. 2006;1(6):3159-65. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.378. Nat Protoc. 2006. PMID: 17406579
-
Analytical methods to investigate glutathione and related compounds in biological and pathological processes.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002 Dec 5;781(1-2):181-206. doi: 10.1016/s1570-0232(02)00618-9. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 12450659 Review.
Cited by
-
Bile acids profile and redox status in healthy infants.Pediatr Res. 2023 Jun;93(7):1856-1864. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02350-y. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 36272998
-
Protective effect of heme oxygenase induction in ethinylestradiol-induced cholestasis.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 May;19(5):924-33. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12401. Epub 2015 Feb 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25683492 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic determination of cell fate through selective inheritance of mitochondria.Nat Cell Biol. 2022 Feb;24(2):148-154. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00837-0. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Nat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35165416 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress markers and antioxidant activity in patients admitted to Intensive Care Unit with acute myocardial infarction.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018 Sep-Oct;12(5):14-19. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2018. PMID: 30202403 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic preconditioning modulates the DNA methylation process of the rat heart to provide tolerance to withstand ischemia reperfusion injury and its associated mitochondrial dysfunction.3 Biotech. 2024 Apr;14(4):121. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-03965-0. Epub 2024 Mar 26. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38550905
References
-
- Kaplowitz N, Aw TY, Ookhtens M. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:715–744. - PubMed
-
- Fujikawa M, Kamiike W, Hatanaka N, Shimizu S, Akashi A, Miyata M, Kurosawa K, Yoshida Y, Tagawa K, Matsuda H. J Surg Res. 1994;57:569–573. - PubMed
-
- Sies H, Koch OR, Martino E, Boveris A. FEBS Lett. 1979;103:287–290. - PubMed
-
- Richie JP, Jr, Lang CA. Anal Biochem. 1987;163:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Reed DJ, Babson JR, Beatty PW, Brodie AE, Ellis WW, Potter DW. Anal Biochem. 1980;106:55–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

