Mutations that cause osteoglophonic dysplasia define novel roles for FGFR1 in bone elongation
- PMID: 15625620
- PMCID: PMC1196382
- DOI: 10.1086/427956
Mutations that cause osteoglophonic dysplasia define novel roles for FGFR1 in bone elongation
Abstract
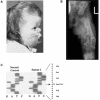
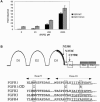
Activating mutations in the genes for fibroblast growth factor receptors 1-3 (FGFR1-3) are responsible for a diverse group of skeletal disorders. In general, mutations in FGFR1 and FGFR2 cause the majority of syndromes involving craniosynostosis, whereas the dwarfing syndromes are largely associated with FGFR3 mutations. Osteoglophonic dysplasia (OD) is a "crossover" disorder that has skeletal phenotypes associated with FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 mutations. Indeed, patients with OD present with craniosynostosis, prominent supraorbital ridge, and depressed nasal bridge, as well as the rhizomelic dwarfism and nonossifying bone lesions that are characteristic of the disorder. We demonstrate here that OD is caused by missense mutations in highly conserved residues comprising the ligand-binding and transmembrane domains of FGFR1, thus defining novel roles for this receptor as a negative regulator of long-bone growth.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical spectrum of fibroblast growth factor receptor mutations.Hum Mutat. 1999;14(2):115-25. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1999)14:2<115::AID-HUMU3>3.0.CO;2-2. Hum Mutat. 1999. PMID: 10425034
-
Osteoglophonic Dysplasia: Phenotypic and Radiological Clues.J Pediatr Genet. 2017 Dec;6(4):247-251. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1602816. Epub 2017 May 5. J Pediatr Genet. 2017. PMID: 29147600 Free PMC article.
-
Fgfr1 and Fgfr2 have distinct differentiation- and proliferation-related roles in the developing mouse skull vault.Development. 1999 Dec;126(24):5611-20. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.24.5611. Development. 1999. PMID: 10572038
-
Craniosynostosis and related limb anomalies.Novartis Found Symp. 2001;232:122-33; discussion 133-43. doi: 10.1002/0470846658.ch9. Novartis Found Symp. 2001. PMID: 11277076 Review.
-
[The molecular genetic background of hereditary craniosynostoses and chondrodysplasias].Ugeskr Laeger. 2001 Sep 3;163(36):4862-7. Ugeskr Laeger. 2001. PMID: 11571861 Review. Danish.
Cited by
-
Antibody-mediated activation of FGFR1 induces FGF23 production and hypophosphatemia.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057322. Epub 2013 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23451204 Free PMC article.
-
FGF receptor-4 (FGFR4) polymorphism acts as an activity switch of a membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-FGFR4 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 7;107(36):15786-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914459107. Epub 2010 Aug 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20798051 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal eruption of teeth in relation to FGFR1 heterozygote mutation: a rare case of osteoglophonic dysplasia with 4-year follow-up.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Feb 11;22(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02069-6. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 35148738 Free PMC article.
-
A missense mutation in Fgfr1 causes ear and skull defects in hush puppy mice.Mamm Genome. 2011 Jun;22(5-6):290-305. doi: 10.1007/s00335-011-9324-8. Epub 2011 Apr 10. Mamm Genome. 2011. PMID: 21479780 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Hyperphosphatemia and Vascular Calcification Are Reduced by Stable Delivery of Soluble Klotho.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Apr;28(4):1162-1174. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015111266. Epub 2016 Nov 11. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27837149 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for OD) - PubMed
References
-
- Anderson J, Burns HD, Enriquez-Harris P, Wilkie AO, Heath JK (1998) Apert syndrome mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 exhibit increased affinity for FGF ligand. Hum Mol Genet 7:1475–1483 - PubMed
-
- Beighton P, Cremin BJ, Kozlowski K (1980) Osteoglophonic dwarfism. Pediatr Radiol 10:46–50 - PubMed
-
- Delezoide AL, Benoist-Lasselin C, Legeai-Mallet L, Le Merrer M, Munnich A, Vekemans M, Bonaventure J (1998) Spatio-temporal expression of FGFR 1, 2 and 3 genes during human embryo-fetal ossification. Mech Dev 77:19–30 - PubMed
-
- Deng C, Wynshaw-Boris A, Zhou F, Kuo A, Leder P (1996) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a negative regulator of bone growth. Cell 84:911–921 - PubMed
-
- Deng CX, Wynshaw-Boris A, Shen MM, Daugherty C, Ornitz DM, Leder P (1994) Murine FGFR-1 is required for early postimplantation growth and axial organization. Genes Dev 8:3045–3057 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

