Modulation of retinoid signaling by a cytoplasmic viral protein via sequestration of Sp110b, a potent transcriptional corepressor of retinoic acid receptor, from the nucleus
- PMID: 14559998
- PMCID: PMC207568
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.21.7498-7509.2003
Modulation of retinoid signaling by a cytoplasmic viral protein via sequestration of Sp110b, a potent transcriptional corepressor of retinoic acid receptor, from the nucleus
Abstract
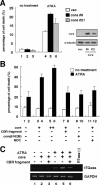
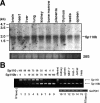
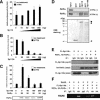
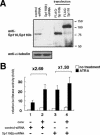
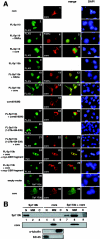
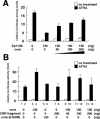
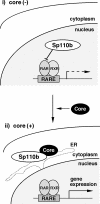
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein (core) plays a significant role in the development of chronic liver diseases caused by HCV infection. We have discovered that the core sensitized all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced cell death in MCF-7 cells. Activation of retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARalpha)-mediated transcription by the core was also seen in all the cell lines tested. By use of a yeast two-hybrid system, we identified Sp110b as a candidate for a core-interacting cellular factor. Although the function of Sp110b has remained unknown, we observed that Sp110b interacts with RARalpha and suppresses RARalpha-mediated transcription. These data suggest that Sp110b is a transcriptional cofactor negatively regulating RARalpha-mediated transcription. RNA interference-mediated reduction of endogenous Sp110b levels depressed the ability of the core to activate RARalpha-mediated transcription, suggesting an essential role for Sp110b in this pathway. The normal nuclear subcellular localization of Sp110b was altered by molecular interaction with the core to the cytoplasmic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. This evidence suggests a model in which the core sequesters Sp110b from the nucleus and inactivates its corepressor function to activate RARalpha-mediated transcription. These findings likely describe a novel system in which a cytoplasmic viral protein regulates host cell transcription.
Figures
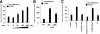

Similar articles
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone inhibits all-trans-retinoic acid-induced retinoic acid receptor alpha nuclear localization and transcriptional activation in mouse Sertoli cell lines.J Biol Chem. 2000 Feb 11;275(6):4145-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.6.4145. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10660575
-
Retinoic acid exerts dual regulatory actions on the expression and nuclear localization of interferon regulatory factor-1.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006 May;231(5):619-31. doi: 10.1177/153537020623100517. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006. PMID: 16636311 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of STAT5b-RARalpha, a novel acute promyelocytic leukemia fusion protein, with retinoic acid receptor and STAT3 signaling pathways.Blood. 2002 Apr 15;99(8):2637-46. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.8.2637. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11929748
-
Ubiquitinated or sumoylated retinoic acid receptor alpha determines its characteristic and interacting model with retinoid X receptor alpha in gastric and breast cancer cells.J Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Jun;32(3):595-613. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0320595. J Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15171703
-
Regulation of CD8(+) T cell functions by RARgamma.Semin Immunol. 2009 Feb;21(1):2-7. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2008.07.002. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Semin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18715802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PPARs and HCV-Related Hepatocarcinoma: A Mitochondrial Point of View.PPAR Res. 2012;2012:605302. doi: 10.1155/2012/605302. Epub 2012 Aug 16. PPAR Res. 2012. PMID: 22966221 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of hepatitis C virus proteins in modulation of cellular functions: a novel action mechanism of the HCV core protein on gene regulation by nuclear hormone receptors.Cancer Sci. 2003 Nov;94(11):937-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01381.x. Cancer Sci. 2003. PMID: 14611668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No associations of human pulmonary tuberculosis with Sp110 variants.J Med Genet. 2006 Jul;43(7):e32. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2005.037960. J Med Genet. 2006. PMID: 16816019 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between HCV and nuclear receptor-mediated pathways.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Oct;132(1):30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 May 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21620888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular characterization of Sp110 gene in pigs.Mol Genet Genomics. 2016 Jun;291(3):1431-42. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1189-9. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Mol Genet Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26995495
References
-
- Alter, H. J., R. H. Purcell, J. W. Shih, J. C. Melpolder, M. Houghton, Q. L. Choo, and G. Kuo. 1989. Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in prospectively followed transfusion recipients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 321:1494-1500. - PubMed
-
- Arany, Z., D. Newsome, E. Oldread, D. M. Livingston, and R. Eckner. 1995. A family of transcriptional adaptor proteins targeted by the E1A oncoprotein. Nature 374:81-84. - PubMed
-
- Ariumi, Y., A. Kaida, M. Hatanaka, and K. Shimotohno. 2001. Functional cross-talk of HIV-1 Tat with p53 through its C-terminal domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 287:556-561. - PubMed
-
- Ariumi, Y., A. Kaida, J. Y. Lin, M. Hirota, O. Masui, S. Yamaoka, Y. Taya, and K. Shimotohno. 2000. HTLV-1 tax oncoprotein represses the p53-mediated trans-activation function through coactivator CBP sequestration. Oncogene 19:1491-1499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
