Cardiotrophin-like cytokine/cytokine-like factor 1 is an essential trophic factor for lumbar and facial motoneurons in vivo
- PMID: 14523086
- PMCID: PMC6740395
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-26-08854.2003
Cardiotrophin-like cytokine/cytokine-like factor 1 is an essential trophic factor for lumbar and facial motoneurons in vivo
Abstract
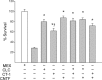
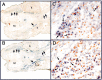
The ciliary neurotrophic factor alpha-receptor (CNTFRalpha) is required for motoneuron survival during development, but the relevant ligand(s) has not been determined. One candidate is the heterodimer formed by cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC) and cytokine-like factor 1 (CLF). CLC/CLF binds to CNTFRalpha and enhances the survival of developing motoneurons in vitro; whether this novel trophic factor plays a role in neural development in vivo has not been tested. We examined motor and sensory neurons in embryonic chicks treated with CLC and in mice with a targeted deletion of the clf gene. Treatment with CLC increased the number of lumbar spinal cord motoneurons that survived the cell death period in chicks. However, this effect was regionally specific, because brachial and thoracic motoneurons were unaffected. Similarly, newborn clf-/- mice exhibited a significant reduction in lumbar motoneurons, with no change in the brachial or thoracic cord. Clf deletion also affected brainstem motor nuclei in a regionally specific manner; the number of motoneurons in the facial but not hypoglossal nucleus was significantly reduced. Sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglia were not affected by either CLC treatment or clf gene deletion. Finally, mRNA for both clc and clf was found in skeletal muscle fibers of embryonic mice during the motoneuron cell death period. These findings support the view that CLC/CLF is a target-derived factor required for the survival of specific pools of motoneurons. The in vivo actions of CLC and CLF can account for many of the effects of CNTFRalpha on developing motoneurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiotrophin-1, a muscle-derived cytokine, is required for the survival of subpopulations of developing motoneurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Feb 15;21(4):1283-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-04-01283.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160399 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-Like Factor 1, an Essential Facilitator of Cardiotrophin-Like Cytokine:Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Receptor α Signaling and sorLA-Mediated Turnover.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Mar 31;36(8):1272-86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00917-15. Print 2016 Apr. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26858303 Free PMC article.
-
The cytokines cardiotrophin-like cytokine/cytokine-like factor-1 (CLC/CLF) and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) differ in their receptor specificities.Cytokine. 2012 Dec;60(3):653-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.08.014. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Cytokine. 2012. PMID: 22986012
-
Developmental motoneuron cell death and neurotrophic factors.Cell Tissue Res. 2000 Jul;301(1):71-84. doi: 10.1007/s004410000217. Cell Tissue Res. 2000. PMID: 10928282 Review.
-
Neurotrophic interactions in the development of spinal cord motoneurons.Ciba Found Symp. 1988;138:152-71. doi: 10.1002/9780470513675.ch10. Ciba Found Symp. 1988. PMID: 3058426 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell proliferation and interleukin-6-type cytokine signaling are implicated by gene expression responses in early optic nerve head injury in rat glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Jan 25;52(1):504-18. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5317. Print 2011 Jan. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 20847120 Free PMC article.
-
CRLF1 promotes malignant phenotypes of papillary thyroid carcinoma by activating the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Mar 7;9(3):371. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0352-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29515111 Free PMC article.
-
Trophic factors as modulators of motor neuron physiology and survival: implications for ALS therapy.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Feb 28;8:61. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00061. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24616665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRLF1 and CLCF1 in Development, Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 17;23(2):992. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020992. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine-like factor 1 (CLF1): life after development?Cytokine. 2011 Sep;55(3):325-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.05.021. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Cytokine. 2011. PMID: 21715184 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander WS, Rakar S, Robb L, Farley A, Willson TA, Zhang J-G, Hartley L, Kikuchi Y, Kojima T, Nomura H, Hasegawa M, Maeda M, Fabri L, Jachno K, Nash A, Metcalf D, Nicola NA, Hilton D ( 1999) Suckling defect in mice lacking the soluble haemopoietin receptor NR6. Curr Biol 9: 605-608. - PubMed
-
- Carroll P, Gayet O, Feuillet C, Kallenbach S, de Bovis B, Dudley K, Alonso S ( 2001) Juxtaposition of CNR protocadherins and reelin expression in the developing spinal cord. Mol Cell Neurosci 17: 611-623. - PubMed
-
- Clarke PG, Oppenheim RW ( 1995) Neuron death in vertebrate development: in vitro methods. Methods Cell Biol 46: 277-321. - PubMed
-
- DeChiara TM, Vesjada R, Poueymirou WT, Acheson A, Suri C, Conover JC, Friedman B, McClain J, Pan L, Stahl N, Ip N, Kato A, Yancopoulos GD ( 1995) Mice lacking the CNTF receptor, unlike mice lacking CNTF, exhibit profound motor neuron deficits at birth. Cell 83: 313-322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
