Brain MR imaging in neonatal hyperammonemic encephalopathy resulting from proximal urea cycle disorders
- PMID: 12812952
- PMCID: PMC8148992
Brain MR imaging in neonatal hyperammonemic encephalopathy resulting from proximal urea cycle disorders
Abstract
We present brain MR images in three patients with neonatal-onset hyperammonemic encephalopathy resulting from urea-cycle disorders (two sisters with deficiency of the carbamyl phosphate synthetase I reaction step and one boy with an ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency). MR imaging revealed almost identical findings of injury to the bilateral lentiform nuclei and the deep sulci of the insular and perirolandic regions; to our knowledge, this pattern has not been previously reported. We hypothesize that these lesions presumably reflect the distribution of brain injury due to hypoperfusion secondary to hyperammonemia and hyperglutaminemia in the neonatal period.
Figures
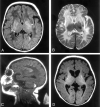
Similar articles
-
Brain MR imaging in acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy arising from late-onset ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003 Mar;24(3):390-3. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. PMID: 12637287 Free PMC article.
-
Carbamyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency: a destructive encephalopathy.Pediatr Neurol. 2001 Mar;24(3):193-9. doi: 10.1016/s0887-8994(00)00259-9. Pediatr Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11301219
-
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency in females: an often overlooked cause of treatable encephalopathy.J Child Neurol. 1995 Sep;10(5):369-74. doi: 10.1177/088307389501000506. J Child Neurol. 1995. PMID: 7499756
-
Unmasked adult-onset urea cycle disorders in the critical care setting.Crit Care Clin. 2005 Oct;21(4 Suppl):S1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2005.05.002. Crit Care Clin. 2005. PMID: 16227111 Review.
-
Genetic counseling issues in urea cycle disorders.Crit Care Clin. 2005 Oct;21(4 Suppl):S37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2005.08.001. Crit Care Clin. 2005. PMID: 16227114 Review.
Cited by
-
The phenotypic spectrum of organic acidurias and urea cycle disorders. Part 2: the evolving clinical phenotype.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015 Nov;38(6):1059-74. doi: 10.1007/s10545-015-9840-x. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015. PMID: 25875216
-
Acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy in adults: imaging findings.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011 Feb;32(2):413-8. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2290. Epub 2010 Nov 18. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 21087942 Free PMC article.
-
1H-MR Spectroscopy of the Early Developmental Brain, Neonatal Encephalopathies, and Neurometabolic Disorders.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2022 Mar 1;21(1):9-28. doi: 10.2463/mrms.rev.2021-0055. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34421092 Free PMC article.
-
[Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of ornithine trans-carbamylase deficiency].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Oct 25;49(5):539-547. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.04.11. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 33210478 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Morphological changes of cortical pyramidal neurons in hepatic encephalopathy.BMC Neurosci. 2014 Jan 17;15:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-15-15. BMC Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24433342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brusilow SW, Horwich AL. Urea cycle enzymes. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, eds. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2001. :1909–1963
-
- Sperl W, Felber S, Skladal D, Wermuth B. Metabolic stroke in carbamyl phosphate synthetase deficiency. Neuropediatrics 1997;28:229–234 - PubMed
-
- Connelly A, Cross JH, Gadian DG, Hunter JV, Kirkham FJ, Leonard JV. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy shows increased brain glutamine in ornithine carbamoyl transferase deficiency. Pediatr Res 1993;33:73–81 - PubMed
-
- Bajaj SK, Kurlemann G, Schuierer G, Peters PE. CT and MRI in a girl with late-onset ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: case report. Neuroradiology 1996;38:796–799 - PubMed
-
- Mirowitz SA, Sartor K, Prensky AJ, Gado M, Hodges FJ III. Neurodegenerative disease of childhood: MR and CT evaluation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1991;15:210–222 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
