Analyses of mrp genes during Myxococcus xanthus development
- PMID: 11698359
- PMCID: PMC95511
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.23.6733-6739.2001
Analyses of mrp genes during Myxococcus xanthus development
Abstract
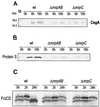
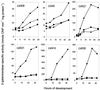
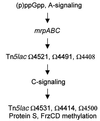
Myxococcus xanthus is a gram-negative soil bacterium that undergoes development under starvation conditions. Our previous study identified a new genetic locus, mrp, which is required for both fruiting body formation and sporulation. The locus encodes two transcripts: mrpAB, which consists of a histidine kinase and an NtrC-like response regulator, and mrpC, a cyclic AMP receptor protein family transcription activator. In this study, we used genetic and biochemical analyses to investigate the possible interactions between the mrp genes and other known developmental genes and events. These studies show that the mrp genes possibly function after A-signaling and (p)ppGpp but before C-signaling and that they regulate various early and late developmental genes and events.
Figures
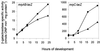

Similar articles
-
Genetic studies of mrp, a locus essential for cellular aggregation and sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2001 Aug;183(16):4786-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.16.4786-4795.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11466282 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulation with Ser/Thr kinase cascade and a His/Asp TCS in Myxococcus xanthus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:111-21. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792684 Review.
-
Transcription factor MrpC binds to promoter regions of hundreds of developmentally-regulated genes in Myxococcus xanthus.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 16;15:1123. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1123. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25515642 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an activator protein required for the induction of fruA, a gene essential for fruiting body development in Myxococcus xanthus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 22;100(15):8782-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1533026100. Epub 2003 Jul 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12851461 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-cell interactions that direct fruiting body development in Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):363-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80301-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991. PMID: 1840894 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome dynamics of the Myxococcus xanthus multicellular developmental program.Elife. 2019 Oct 14;8:e50374. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50374. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31609203 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems That Regulate the Temporal and Spatial Expression of Myxococcus xanthus Sporulation Genes.J Bacteriol. 2015 Sep 14;198(3):377-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.00474-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26369581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutation of self-binding sites in the promoter of the MrpC transcriptional regulator leads to asynchronous Myxococcus xanthus development.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 23;14:1293966. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1293966. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38075919 Free PMC article.
-
Role of sigmaD in regulating genes and signals during Myxococcus xanthus development.J Bacteriol. 2006 May;188(9):3246-56. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.9.3246-3256.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16621817 Free PMC article.
-
EspA, an orphan hybrid histidine protein kinase, regulates the timing of expression of key developmental proteins of Myxococcus xanthus.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jul;190(13):4416-26. doi: 10.1128/JB.00265-08. Epub 2008 Apr 4. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18390653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campos J M, Geisselsoder J, Zusman D R. Isolation of bacteriophage Mx4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978;119:167–178. - PubMed
-
- Cashel M, Rudd K E. The stringent response. In: Neidhardt F C, Low K, Magasanick B, Schaechter M, Umbarger H, editors. Esherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. Vol. 2. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press; 1987. pp. 1410–1438.
-
- Cho K, Zusman D R. AsgD, a new two-component regulator required for A-signaling and nutrient sensing during early development of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Microbiol. 1999;34:268–281. - PubMed
-
- Downard J, Toal D. Branched-chain fatty acids: the case for a novel form of cell-cell signalling during Myxococcus xanthus development. Mol Microbiol. 1995;16:171–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

