Identification of the gene for oral-facial-digital type I syndrome
- PMID: 11179005
- PMCID: PMC1274470
- DOI: 10.1086/318802
Identification of the gene for oral-facial-digital type I syndrome
Abstract
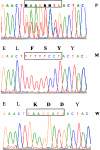
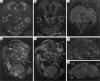
Oral-facial-digital type 1 syndrome (OFD1 [MIM 311200]) is transmitted as an X-linked dominant condition with lethality in males and is characterized by malformations of the face, oral cavity, and digits, and by a highly variable expressivity even within the same family. Malformation of the brain and polycystic kidneys are commonly associated with this disorder. The locus for OFD1 was mapped by linkage analysis to a 12-Mb interval, flanked by markers DXS85 and DXS7105 in the Xp22 region. To identify the gene responsible for this syndrome, we analyzed several transcripts mapping to the region and found mutations in OFD1 (formerly named "Cxorf5/71-7a"), encoding a protein containing coiled-coil alpha-helical domains. Seven patients with OFD1, including three with familial and four with sporadic cases, were analyzed. Analysis of the familial cases revealed a missense mutation, a 19-bp deletion, and a single base-pair deletion leading to a frameshift. In the sporadic cases, we found a missense (de novo), a nonsense, a splice, and a frameshift mutation. RNA in situ studies on mouse embryo tissue sections show that Ofd1 is developmentally regulated and is expressed in all tissues affected in OFD1 syndrome. The involvement of OFD1 in oral-facial-digital type I syndrome demonstrates an important role of this gene in human development.
Figures
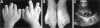

Similar articles
-
A novel mutation in the OFD1 (Cxorf5) gene may contribute to oral phenotype in patients with oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1.Oral Dis. 2011 Sep;17(6):610-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2011.01823.x. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Oral Dis. 2011. PMID: 21729220
-
The oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1 (OFD1), a cause of polycystic kidney disease and associated malformations, maps to Xp22.2-Xp22.3.Hum Mol Genet. 1997 Jul;6(7):1163-7. doi: 10.1093/hmg/6.7.1163. Hum Mol Genet. 1997. PMID: 9215688
-
Clinical, molecular, and genotype-phenotype correlation studies from 25 cases of oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1: a French and Belgian collaborative study.J Med Genet. 2006 Jan;43(1):54-61. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2004.027672. J Med Genet. 2006. PMID: 16397067 Free PMC article.
-
Joint dislocation and cerebral anomalies are consistently associated with oral-facial-digital syndrome type IV.Clin Genet. 1995 Sep;48(3):156-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1995.tb04077.x. Clin Genet. 1995. PMID: 8556824 Review.
-
Oral-facial-digital syndromes, 1992.Clin Dysmorphol. 1993 Apr;2(2):95-105. Clin Dysmorphol. 1993. PMID: 8281288 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel X-linked recessive mental retardation syndrome comprising macrocephaly and ciliary dysfunction is allelic to oral-facial-digital type I syndrome.Hum Genet. 2006 Sep;120(2):171-8. doi: 10.1007/s00439-006-0210-5. Epub 2006 Jun 17. Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16783569
-
Expanding the phenotype of males with OFD1 pathogenic variants-a case report and literature review.Eur J Med Genet. 2022 Jun;65(6):104496. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2022.104496. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Eur J Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 35398350 Free PMC article.
-
Autistic Behavior as Novel Clinical Finding in OFD1 Syndrome.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;14(2):327. doi: 10.3390/genes14020327. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833254 Free PMC article.
-
The ciliary Frizzled-like receptor Tmem67 regulates canonical Wnt/β-catenin signalling in the developing cerebellum via Hoxb5.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 1;9(1):5446. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41940-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30931988 Free PMC article.
-
Oral-facial-digital syndrome type 1 in males: Congenital heart defects are included in its phenotypic spectrum.Am J Med Genet A. 2017 May;173(5):1383-1389. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38179. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Am J Med Genet A. 2017. PMID: 28371265 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Expressed Sequence Tags database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/dbEST/index.html
-
- GenBank Overview, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankOverview.html (for OFD1 locus [accession number AC003037], OFD1 [accession numbers Y15164 and Y16355], and mouse EST [accession number AJ278702])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for OFD1 [MIM 311200]) - PubMed
-
- TIGEM, http://www.tigem.it/
References
-
- Adler DA, Rugarli EI, Lingenfelter PA, Tsuchiya K, Poslinski D, Liggitt HD, Chapman VM, Elliott RW, Ballabio A, Disteche CM (1997) Evidence of evolutionary up-regulation of the single active X chromosome in mammals based on Clc4 expression levels in Mus spretus and Mus musculus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9244–9248 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonarakis SE (1998) Recommendations for a nomenclature system for human gene mutations. Nomenclature Working Group. Hum Mutat 11:1–3 - PubMed
-
- Buchner G, Orfanelli U, Quaderi N, Bassi MT, Andolfi G, Ballabio A, Franco B (2000) Identification of a new EGF-repeat-containing gene from human Xp22: a candidate for developmental disorders. Genomics 65:16–23 - PubMed
-
- Coll E, Torra R, Pascual J, Botey A, Ara J, Perez L, Ballesta F, Darnell A (1997) Sporadic orofaciodigital syndrome type I presenting as end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:1040–1042 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

