Brain involvement in Salla disease
- PMID: 10219409
- PMCID: PMC7056084
Brain involvement in Salla disease
Abstract
Background and purpose: Our purpose was to document the nature and progression of brain abnormalities in Salla disease, a lysosomal storage disorder, with MR imaging.
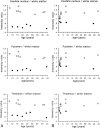
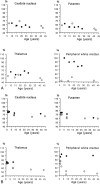
Methods: Fifteen patients aged 1 month to 43 years underwent 26 brain MR examinations. In 10 examinations, signal intensity was measured and compared with that of healthy volunteers of comparable ages.
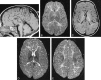
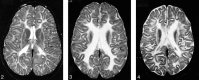
Results: MR images of a 1-month-old asymptomatic child showed no pathology. In all other patients, abnormal signal intensity was found: on T2-weighted images, the cerebral white matter had a higher signal intensity than the gray matter, except in the internal capsules. In six patients, the white matter was homogeneous on all images. In four patients, the periventricular white matter showed a somewhat lower signal intensity; in five patients, a higher signal intensity. In the peripheral cerebral white matter, the measured signal intensity remained at a high level throughout life. No abnormalities were seen in the cerebellar white matter. Atrophic changes, if present, were relatively mild but were found even in the cerebellum and brain stem. The corpus callosum was always thin.
Conclusion: In Salla disease, the cerebral myelination process is defective. In some patients, a centrifugally progressive destructive process is also seen in the cerebral white matter. Better myelination in seen in patients with milder clinical symptoms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MR imaging of the developing human brain. Part 2. Postnatal development.Radiographics. 1993 May;13(3):611-22. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.13.3.8316668. Radiographics. 1993. PMID: 8316668
-
MR of childhood metachromatic leukodystrophy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997 Apr;18(4):733-8. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997. PMID: 9127040 Free PMC article.
-
MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic studies in Sjögren-Larsson syndrome: characterization of the leukoencephalopathy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004 Apr;25(4):649-57. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. PMID: 15090362 Free PMC article.
-
Globoid cell leukodystrophy: distinguishing early-onset from late-onset disease using a brain MR imaging scoring method.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999 Feb;20(2):316-23. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. PMID: 10094363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRI of the brain in the Kearns-Sayre syndrome: report of four cases and a review.Neuroradiology. 1999 Oct;41(10):759-64. doi: 10.1007/s002340050838. Neuroradiology. 1999. PMID: 10552027 Review.
Cited by
-
An Unusual Developmental Profile of Salla Disease in a Patient with the SallaFIN Mutation.Case Rep Neurol Med. 2012;2012:615721. doi: 10.1155/2012/615721. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2012. PMID: 23227378 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of wild-type and mutant human sialin.EMBO J. 2004 Nov 24;23(23):4560-70. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600464. Epub 2004 Oct 28. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15510212 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging pattern recognition in hypomyelinating disorders.Brain. 2010 Oct;133(10):2971-82. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq257. Brain. 2010. PMID: 20881161 Free PMC article.
-
Sialic acids in the brain: gangliosides and polysialic acid in nervous system development, stability, disease, and regeneration.Physiol Rev. 2014 Apr;94(2):461-518. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00033.2013. Physiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24692354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychiatric symptoms in Salla disease.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2023 Oct;32(10):2043-2047. doi: 10.1007/s00787-022-02031-5. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 35796883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aula P, Autio S, Raivio KO. “Salla disease”: a new lysosomal storage disorder. Arch Neurol 1979;36:88-94 - PubMed
-
- Renlund M, Aula P, Raivio KO, et al. Salla disease: a new lysosomal disorder with disturbed sialic acid metabolism. Neurology 1983;33:57-66 - PubMed
-
- Renlund M, Tietze F, Gahl WA. Defective sialic acid egress from isolated fibroblast lysosomes of patients with Salla disease. Science 1986;232:759-762 - PubMed
-
- Haataja L, Parkkola R, Sonninen P, et al. Phenotypic variation and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in Salla disease, a free sialic acid storage disorder. Neuropediatrics 1994;25:1-7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
