Mammalian capping enzyme complements mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacking mRNA guanylyltransferase and selectively binds the elongating form of RNA polymerase II
- PMID: 9371772
- PMCID: PMC24235
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.12898
Mammalian capping enzyme complements mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacking mRNA guanylyltransferase and selectively binds the elongating form of RNA polymerase II
Abstract
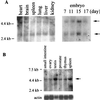
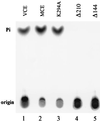
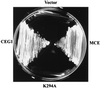
5'-Capping is an early mRNA modification that has important consequences for downstream events in gene expression. We have isolated mammalian cDNAs encoding capping enzyme. They contain the sequence motifs characteristic of the nucleotidyl transferase superfamily. The predicted mouse and human enzymes consist of 597 amino acids and are 95% identical. Mouse cDNA directed synthesis of a guanylylated 68-kDa polypeptide that also contained RNA 5'-triphosphatase activity and catalyzed formation of RNA 5'-terminal GpppG. A haploid strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacking mRNA guanylyltransferase was complemented for growth by the mouse cDNA. Conversion of Lys-294 in the KXDG-conserved motif eliminated both guanylylation and complementation, identifying it as the active site. The K294A mutant retained RNA 5'-triphosphatase activity, which was eliminated by N-terminal truncation. Full-length capping enzyme and an active C-terminal fragment bound to the elongating form and not to the initiating form of polymerase. The results document functional conservation of eukaryotic mRNA guanylyltransferases from yeast to mammals and indicate that the phosphorylated C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II couples capping to transcription elongation. These results also explain the selective capping of RNA polymerase II transcripts.
Figures




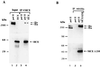
Comment in
-
Origins of mRNA identity: capping enzymes bind to the phosphorylated C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Nov 25;94(24):12758-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.24.12758. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9398072 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A yeast-based genetic system for functional analysis of viral mRNA capping enzymes.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(12):5486-94. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.12.5486-5494.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10823853 Free PMC article.
-
The guanylyltransferase domain of mammalian mRNA capping enzyme binds to the phosphorylated carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II.J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 17;273(16):9577-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.16.9577. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9545288
-
Covalent catalysis in nucleotidyl transfer reactions: essential motifs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA capping enzyme are conserved in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and viral capping enzymes and among polynucleotide ligases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12046-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12046. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 7991582 Free PMC article.
-
RNA capping enzyme and DNA ligase: a superfamily of covalent nucleotidyl transferases.Mol Microbiol. 1995 Aug;17(3):405-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17030405.x. Mol Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8559059 Review.
-
Capping enzyme in eukaryotic mRNA synthesis.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1995;50:101-29. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60812-0. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7754031 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Enzymatic Protein Biopolymers as a Tool to Synthetize Eukaryotic Messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA) with Uses in Vaccination, Immunotherapy and Nanotechnology.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jul 23;12(8):1633. doi: 10.3390/polym12081633. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32717794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cet1-Ceg1 mRNA capping apparatus.Structure. 2010 Feb 10;18(2):216-27. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.12.009. Structure. 2010. PMID: 20159466 Free PMC article.
-
The Tat/TAR-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain stimulates cotranscriptional capping of HIV-1 mRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12666-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1835726100. Epub 2003 Oct 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14569024 Free PMC article.
-
The essential role for the RNA triphosphatase Cet1p in nuclear import of the mRNA capping enzyme Cet1p-Ceg1p complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 30;8(10):e78000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078000. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205062 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide yields mechanistic insights into human mRNA capping enzyme function.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 13;12(10):e0186423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186423. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29028835 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

