Unlocking the potential of Kluyveromyces marxianus in the definition of aroma composition of cheeses
- PMID: 39360317
- PMCID: PMC11445029
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1464953
Unlocking the potential of Kluyveromyces marxianus in the definition of aroma composition of cheeses
Abstract
Introduction: The cheese microbiota is very complex and is made up of technologically-relevant, spoilage, opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms. Among them lactic acid bacteria and yeasts are the main ones. One of the most interesting dairy yeasts is Kluyveromyces marxianus because of its technological properties including the ability to produce aroma compounds.
Methods: This study investigated the contribution of Kluyveromyces marxianus to the gross composition and aroma profile of cow cheeses. Experimental cheeses were prepared by inoculating a co-culture of K. marxianus FM09 and a commercial strain of Lacticaseibacillus casei and compared with cheeses obtained with only L. casei. The gross composition was determined by a FoodScan™ 2 Dairy Analyser, and free amino acids were evaluated at 507 nm after reaction with Cd-ninhydrin. The volatile organic compounds were extracted by head-space solid phase micro-extraction and analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry coupled with odor activity values. qRT-PCR was applied to determine the expression of genes involved in esters synthesis and degradation.
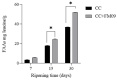
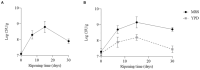
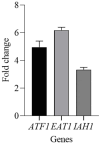
Results: The inoculation of K. marxianus induced an increase of pH and a reduction of protein content of cheeses, in agreement with the stronger proteolysis detected in these cheeses. K. marxianus influenced the content of aroma compounds both quantitatively and qualitatively. In particular, an increase of higher alcohols, esters and organic acids was observed. Moreover, 12 compounds were detected only in cheeses obtained with the co-culture. These differences were in agreement with the odor activity values (OAV). In fact, only 11 compounds showed OAV > 1 in cheeses obtained with the commercial strain, and 24 in those obtained with the co-culture. The qPCR analysis revealed an over expression of ATF1, EAT1, and IAH1 genes.
Conclusion: Kluyveromyces marxianus could act as an important auxiliary starter for cheese production through the development and diversification of compounds related to flavor in short-aged cow cheeses.
Keywords: Kluyveromyces marxianus; OAV; aroma compounds; cheese; qPCR.
Copyright © 2024 Perpetuini, Rossetti, Rapagnetta and Tofalo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosome arrangement, differentiation of growth kinetics and volatile molecule profiles in Kluyveromyces marxianus strains from Italian cheeses.Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 Dec 2;214:151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26310129
-
CRISPRi-induced transcriptional regulation of IAH1 gene and its influence on volatile compounds profile in Kluyveromyces marxianus DU3.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 5;40(4):121. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03811-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38441729
-
Evaluation of the Effect of Auxiliary Starter Yeasts With Enzyme Activities on Kazak Cheese Quality and Flavor.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 16;11:614208. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.614208. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391244 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Yeasts in White-Brined Cheeses: Methodologies for Identification, Spoilage Potential and Good Manufacturing Practices.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 15;11:582778. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.582778. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33178163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cheese yeasts.Yeast. 2019 Mar;36(3):129-141. doi: 10.1002/yea.3368. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Yeast. 2019. PMID: 30512214 Review.
References
-
- Alonso-Vargas M., Téllez-Jurado A., Gómez-Aldapa C. A., Ramírez-Vargas M., Conde-Báez L., Castro-Rosas J., et al. . (2022). Optimization of 2-Phenylethanol production from sweet whey fermentation using Kluyveromyces marxianus. Fermentation 8:39. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8020039 - DOI
-
- Arora G., Cormier F., Lee B. (1995). Analysis of odor-active volatiles in Cheddar cheese headspace by multidimensional GC/MS/sniffing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 43, 748–752. doi: 10.1021/jf00051a035 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

