Collaborative effort: managing Bardet-Biedl syndrome in pediatric patients. Case series and a literature review
- PMID: 39092285
- PMCID: PMC11291331
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1424819
Collaborative effort: managing Bardet-Biedl syndrome in pediatric patients. Case series and a literature review
Abstract
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS) is an autosomal recessive non-motile ciliopathy, caused by mutations in more than twenty genes. Their expression leads to the production of BBSome-building proteins or chaperon-like proteins supporting its structure. The prevalence of the disease is estimated at 1: 140,000 - 160,000 of life births. Its main clinical features are retinal dystrophy, polydactyly, obesity, cognitive impairment, hypogonadism, genitourinary malformations, and kidney disease. BBS is characterized by heterogeneous clinical manifestation and the variable onset of signs and symptoms. We present a case series of eight pediatric patients with BBS (6 boys and 2 girls) observed in one clinical center including two pairs of siblings. The patients' age varies between 2 to 13 years (average age of diagnosis: 22 months). At presentation kidney disorders were observed in seven patients, polydactyly in six patients' obesity, and psychomotor development delay in two patients. In two patients with kidney disorders, the genetic tests were ordered at the age of 1 and 6 months due to the presence of symptoms suggesting BBS and having an older sibling with the diagnosis of the syndrome. The mutations in the following genes were confirmed: BBS10, MKKS, BBS7/BBS10, BBS7, BBS9. All described patients developed symptoms related to the urinary system and kidney-function impairment. Other most common symptoms are polydactyly and obesity. In one patient the obesity class 3 was diagnosed with multiple metabolic disorders. In six patients the developmental delay was diagnosed. The retinopathy was observed only in one, the oldest patient. Despite having the same mutations (siblings) or having mutations in the same gene, the phenotypes of the patients are different. We aimed to addresses gaps in understanding BBS by comparing our data and existing literature through a narrative review. This research includes longitudinal data and explores genotype-phenotype correlations of children with BBS. BBS exhibits diverse clinical features and genetic mutations, making diagnosis challenging despite defined criteria. Same mutations can result in different phenotypes. Children with constellations of polydactyly and/or kidney disorders and/or early-onset obesity should be managed towards BBS. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective monitoring and intervention to manage the multisystemic dysfunctions associated with BBS.
Keywords: BBS; Bardet-Biedl syndrome; genetics; obesity; rare diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Nowak-Ciołek, Ciołek, Tomaszewska, Hildebrandt, Kitzler, Deutsch, Lemberg, Shril, Szczepańska and Zachurzok.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
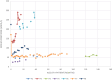
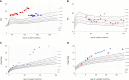
Similar articles
-
Defining the optimum strategy for identifying adults and children with coeliac disease: systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Oct;26(44):1-310. doi: 10.3310/ZUCE8371. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36321689 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of school-based family asthma educational programs on the quality of life and number of asthma exacerbations of children aged five to 18 years diagnosed with asthma: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):69-81. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2335. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571284
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulators and immunosuppressants for multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 6;2013(6):CD008933. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008933.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23744561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- U.S. National Library of Medicine . Bardet-Biedl Syndrome: Medlineplus Genetics. MedlinePlus (2020). Available online at: https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/bardet-biedl-syndrome/#frequency (Accessed January 27, 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

