Large-scale whole-exome sequencing analyses identified protein-coding variants associated with immune-mediated diseases in 350,770 adults
- PMID: 39009607
- PMCID: PMC11250857
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49782-0
Large-scale whole-exome sequencing analyses identified protein-coding variants associated with immune-mediated diseases in 350,770 adults
Abstract
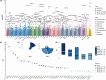
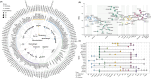
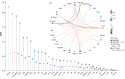
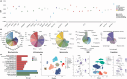
The genetic contribution of protein-coding variants to immune-mediated diseases (IMDs) remains underexplored. Through whole exome sequencing of 40 IMDs in 350,770 UK Biobank participants, we identified 162 unique genes in 35 IMDs, among which 124 were novel genes. Several genes, including FLG which is associated with atopic dermatitis and asthma, showed converging evidence from both rare and common variants. 91 genes exerted significant effects on longitudinal outcomes (interquartile range of Hazard Ratio: 1.12-5.89). Mendelian randomization identified five causal genes, of which four were approved drug targets (CDSN, DDR1, LTA, and IL18BP). Proteomic analysis indicated that mutations associated with specific IMDs might also affect protein expression in other IMDs. For example, DXO (celiac disease-related gene) and PSMB9 (alopecia areata-related gene) could modulate CDSN (autoimmune hypothyroidism-, psoriasis-, asthma-, and Graves' disease-related gene) expression. Identified genes predominantly impact immune and biochemical processes, and can be clustered into pathways of immune-related, urate metabolism, and antigen processing. Our findings identified protein-coding variants which are the key to IMDs pathogenesis and provided new insights into tailored innovative therapies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic landscape of atopic dermatitis.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Oct 1;24(5):409-415. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000001005. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38920356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis.Nat Genet. 2006 Apr;38(4):441-6. doi: 10.1038/ng1767. Epub 2006 Mar 19. Nat Genet. 2006. PMID: 16550169
-
Protein-coding variants contribute to the risk of atopic dermatitis and skin-specific gene expression.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Apr;145(4):1208-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.10.030. Epub 2019 Nov 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31707051
-
Filaggrin loss-of-function mutations as a predictor for atopic eczema, allergic sensitization and eczema-associated asthma in Polish children population.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017 Sep;26(6):991-998. doi: 10.17219/acem/61430. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 29068602
-
Genetics of Atopic Dermatitis: From DNA Sequence to Clinical Relevance.Dermatology. 2019;235(5):355-364. doi: 10.1159/000500402. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Dermatology. 2019. PMID: 31203284 Review.
Cited by
-
Large-scale exome sequencing identified 18 novel genes for neuroticism in 394,005 UK-based individuals.Nat Hum Behav. 2025 Feb;9(2):406-419. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-02045-w. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Nat Hum Behav. 2025. PMID: 39511343
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

