A comprehensive computational benchmark for evaluating deep learning-based protein function prediction approaches
- PMID: 38388682
- PMCID: PMC10883809
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbae050
A comprehensive computational benchmark for evaluating deep learning-based protein function prediction approaches
Abstract
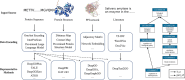
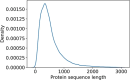
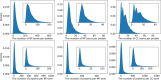
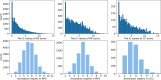
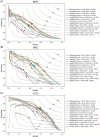
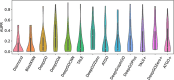
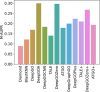
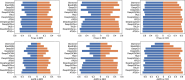
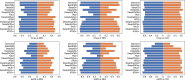
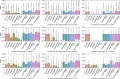
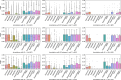
Proteins play an important role in life activities and are the basic units for performing functions. Accurately annotating functions to proteins is crucial for understanding the intricate mechanisms of life and developing effective treatments for complex diseases. Traditional biological experiments struggle to keep pace with the growing number of known proteins. With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology, a wide variety of biological data provides the possibility to accurately predict protein functions by computational methods. Consequently, many computational methods have been proposed. Due to the diversity of application scenarios, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of these computational methods to determine the suitability of each algorithm for specific cases. In this study, we present a comprehensive benchmark, BeProf, to process data and evaluate representative computational methods. We first collect the latest datasets and analyze the data characteristics. Then, we investigate and summarize 17 state-of-the-art computational methods. Finally, we propose a novel comprehensive evaluation metric, design eight application scenarios and evaluate the performance of existing methods on these scenarios. Based on the evaluation, we provide practical recommendations for different scenarios, enabling users to select the most suitable method for their specific needs. All of these servers can be obtained from https://csuligroup.com/BEPROF and https://github.com/CSUBioGroup/BEPROF.
Keywords: benchmark; deep learning; protein; protein function.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
On the objectivity, reliability, and validity of deep learning enabled bioimage analyses.Elife. 2020 Oct 19;9:e59780. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59780. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33074102 Free PMC article.
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Peer Play.2023 Jul 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Jul 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30020595 Free Books & Documents.
-
Exploring conceptual and theoretical frameworks for nurse practitioner education: a scoping review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):146-55. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2150. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571290
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learning model for protein multi-label subcellular localization and function prediction based on multi-task collaborative training.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae568. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae568. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39489606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li M, Ni P, Chen X, et al. . Construction of refined protein interaction network for predicting essential proteins. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 2017;16(4):1386–97. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Meng X, Xiang J, et al. . CACO: a core-attachment method with cross-species functional ortholog information to detect human protein complexes. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 2023;27:4569–78. - PubMed
-
- Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, et al. . Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015;347(6220):1260419. - PubMed

