Mendelian randomization study reveals the relationship between dietary factors and respiratory diseases
- PMID: 38114639
- PMCID: PMC10730871
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-50055-x
Mendelian randomization study reveals the relationship between dietary factors and respiratory diseases
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Mendelian randomization study reveals the relationship between dietary factors and respiratory diseases.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 19;14(1):4101. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53866-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38374127 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
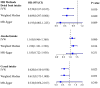
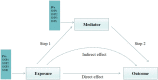
The existence of causal relationship between dietary factors and respiratory diseases is uncertain. We comprehensively investigated the association between dietary factors and respiratory diseases by using Mendelian randomization (MR). Genetic variants linked to dietary factors were selected as instrumental variables with genome-wide significance. These instrumental variables were obtained from large GWAS databases. These databases include Biobank, the FinnGen study, and other large consortia. We used multivariate MR analyses to control the effects of smoking and education. Median analysis was conducted to evaluate whether body mass index (BMI) played a role in dietary factors in respiratory diseases. Dried fruit intake was found to be associated with a decreased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (OR: 0.211; 95% CI 0.117-0.378; P < 0.001) and asthma (OR: 0.539; 95% CI 0.357-0.815; P = 0.003). Conversely, pork intake was associated with an increased risk of international pharmaceutical federation (IPF) (OR: 1.051*102, 95% CI 4.354-2.56*103, P = 0.004). However, no significant associations were observed between the 20 dietary factors and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In addition, multivariate MR analyses showed that the above results were unchanged in smoking and nonsmoking populations, while the effect of dried fruit intake on asthma was significantly attenuated after corrective education. The results of the mediator variable analysis indicated that BMI could serve as a mediator of the above results. This study found that dried fruits slowed the progression of COPD and asthma, while pork promoted IPF. However, no effect of dietary factors on OSA was found. Meanwhile, we showed that the above results were unchanged in smoking and non-smoking populations. In contrast, education could influence the role of diet on asthma, and BMI could be used as a mediating variable to influence the above results.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Causal associations of obstructive sleep apnea with Chronic Respiratory Diseases: a Mendelian Randomization study.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Aug 26;24(1):409. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03228-x. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39187806 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the relationship between sarcopenia and 11 respiratory diseases: a comprehensive mendelian randomization analysis.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Oct 12;36(1):205. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02855-y. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 39395132 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking, Coffee Consumption, Alcohol Intake, and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2023;20(2):280-289. doi: 10.2174/1567202620666230627145908. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 37366363
-
Causal association of rheumatoid arthritis with obstructive lung disease: Evidence from Mendelian randomization study.Heart Lung. 2023 Nov-Dec;62:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2023.05.020. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Heart Lung. 2023. PMID: 37302263
-
[Research progress of Mendelian randomization analysis in obstructive sleep apnea].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jul 7;59(7):774-781. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20240210-00086. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39107130 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Casual effects of telomere length on sarcoidosis: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 17;11:1408980. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1408980. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39086950 Free PMC article.
-
The causal relationship between diet habits and cholelithiasis: a comprehensive Mendelian randomization (MR) study.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 12;11:1377631. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1377631. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38933877 Free PMC article.
-
The Causal Association Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Child-Onset Asthma Come to Light: A Mendelian Randomization Study.Nat Sci Sleep. 2024 Jul 19;16:979-987. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S472014. eCollection 2024. Nat Sci Sleep. 2024. PMID: 39050365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon SB, Bruce NG, Grigg J, Hibberd PL, Kurmi OP, K-bH Lam, Mortimer K, Asante KP, Balakrishnan K, Balmes J, Bar-Zeev N, Bates MN, Breysse PN, Buist S, Chen Z, Havens D, Jack D, Jindal S, Kan H, Mehta S, Moschovis P, Naeher L, Patel A, Perez-Padilla R, Pope D, Rylance J, Semple S, Martin WJ. Respiratory risks from household air pollution in low and middle income countries. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014;2(10):823–860. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70168-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed