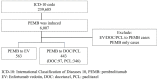
Administration of Enfortumab Vedotin after Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor and the Prognosis in Japanese Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Large Database Study on Enfortumab Vedotin in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma
- PMID: 37686503
- PMCID: PMC10486515
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15174227
Administration of Enfortumab Vedotin after Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor and the Prognosis in Japanese Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Large Database Study on Enfortumab Vedotin in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Enfortumab vedotin shows promise as a targeted therapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma, particularly in patients who have previously received platinum-based chemotherapy and an immune-checkpoint inhibitor. The EV-301 phase III trial demonstrated significantly improved overall survival and response rates compared to standard chemotherapy. However, more data, especially from larger real-world studies, are needed to further assess its effectiveness in Japanese patients.
Methods: A total of 6007 urothelial cancer patients inducted with pembrolizumab as a second-line treatment were analyzed. Among them, 563 patients received enfortumab vedotin after pembrolizumab, while 443 patients received docetaxel or paclitaxel after pembrolizumab, and all were included in the study for efficacy as a life prolonging agent.
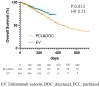
Results: The enfortumab vedotin group showed a longer overall survival than the paclitaxel/docetaxel group (p = 0.013, HR: 0.71). In multivariate analysis, enfortumab vedotin induction was the independent risk factor for overall survival (p = 0.013, HR: 0.70). There were no significant differences in cancer-specific survival.
Conclusions: Enfortumab vedotin prolonged the overall survival for Japanese advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma patients compared to paclitaxel or docetaxel after pembrolizumab treatment.
Keywords: database; enfortumab vedotin; immune checkpoint; real world; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enfortumab Vedotin in Previously Treated Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2021 Mar 25;384(12):1125-1135. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035807. Epub 2021 Feb 12. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 33577729 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Enfortumab vedotin following platinum-based chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced urothelial carcinoma: response, survival and safety analysis from a multicentre real-world Japanese cohort.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024 Mar 9;54(3):329-338. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyad170. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38061911
-
Enfortumab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab in Untreated Advanced Urothelial Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 7;390(10):875-888. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2312117. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38446675 Clinical Trial.
-
Managing potential adverse events during treatment with enfortumab vedotin + pembrolizumab in patients with advanced urothelial cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 22;14:1326715. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1326715. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38711854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab as monotherapies and combination treatment in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: A narrative review.Curr Urol. 2023 Dec;17(4):271-279. doi: 10.1097/CU9.0000000000000204. Epub 2023 May 5. Curr Urol. 2023. PMID: 37994340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enfortumab Vedotin Following Platinum Chemotherapy and Avelumab Maintenance in Patients with Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Retrospective Data from the ARON-2EV Study.Target Oncol. 2024 Nov;19(6):905-915. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01099-0. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Target Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39354179 Free PMC article.
-
C-reactive Protein Is a Prognostic Factor for Survival in Metastatic Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Patients Receiving Pembrolizumab.In Vivo. 2024 Jul-Aug;38(4):1823-1828. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13634. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38936923 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Expression of p53 and FGFR3 Predicts Response to Enfortumab Vedotin in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 26;25(19):10348. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910348. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408678 Free PMC article.
-
C-Reactive Protein Is a Potential Prognostic Marker in Patient with Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Treated with Enfortumab Vedotin: A Multi-Center Retrospective Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 28;16(9):1725. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091725. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alimohamed N., Grewal S., Wirtz H.S., Hepp Z., Sauvageau S., Boyne D.J., Brenner D.R., Cheung W.Y., Jarada T.N. Understanding Treatment Patterns and Outcomes among Patients with De Novo Unresectable Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Cancer: A Population-Level Retrospective Analysis from Alberta, Canada. Curr. Oncol. 2022;29:7587–7597. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29100599. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources