Tafasitamab for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: final 5-year efficacy and safety findings in the phase II L-MIND study
- PMID: 37646664
- PMCID: PMC10828760
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283480
Tafasitamab for patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: final 5-year efficacy and safety findings in the phase II L-MIND study
Abstract
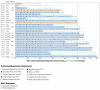
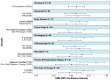
Tafasitamab, an anti-CD19 immunotherapy, is used with lenalidomide for patients with autologous stem cell transplant-ineligible relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma based on the results of the phase II L-MIND study (NCT02399085). We report the final 5-year analysis of this study. Eighty patients ≥18 years who had received one to three prior systemic therapies, and had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0-2 received up to 12 cycles of co-administered tafasitamab and lenalidomide, followed by tafasitamab monotherapy until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was the best objective response rate. Secondary endpoints included duration of response, progression-free survival, overall survival, and safety. Exploratory analyses evaluated efficacy endpoints by prior lines of therapy. At data cutoff on November 14, 2022, the objective response rate was 57.5%, with a complete response rate of 41.3% (n=33), which was consistent with prior analyses. With a median follow-up of 44.0 months, the median duration of response was not reached. The median progression-free survival was 11.6 months (95% confidence interval [95% CI]: 5.7-45.7) with a median follow-up of 45.6 months. The median overall survival was 33.5 months (95% CI: 18.3-not reached) with a median follow-up of 65.6 months. Patients who had received one prior line of therapy (n=40) showed a higher objective response rate (67.5%; 52.5% complete responses) compared to patients who had received two or more prior lines of therapy (n=40; 47.5%; 30% complete responses), but the median duration of response was not reached in either subgroup. Other exploratory analyses revealed consistent long-term efficacy results across subgroups. Adverse events were consistent with those described in previous reports, were manageable, and their frequency decreased during tafasitamab monotherapy, with no new safety concerns. This final 5-year analysis of L-MIND demonstrates that the immunotherapy combination of tafasitamab and lenalidomide is well tolerated and has long-term clinical benefit with durable responses.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (L-MIND): a multicentre, prospective, single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Jul;21(7):978-988. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30225-4. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32511983 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term outcomes from the Phase II L-MIND study of tafasitamab (MOR208) plus lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Haematologica. 2021 Sep 1;106(9):2417-2426. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2020.275958. Haematologica. 2021. PMID: 34196165 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tafasitamab Plus Lenalidomide Versus 3 Rituximab-Based Treatments for Non-Transplant Eligible Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison.Adv Ther. 2022 Jun;39(6):2668-2687. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02094-5. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35403948 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Tafasitamab for the treatment of relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021 Apr;21(4):455-463. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2021.1884677. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33554668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tafasitamab for the treatment of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2309701. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2309701. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38299612 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing of Anti-CD19 Therapies in the Management of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 15;30(14):2895-2904. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-1962. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38661647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The future of immunotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Int J Cancer. 2025 Jan 15;156(2):251-261. doi: 10.1002/ijc.35156. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Int J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39319495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: New Approved Options.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 22;13(1):70. doi: 10.3390/jcm13010070. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38202077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Targets and Advanced Therapies in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 17;16(12):2243. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122243. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927948 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. World Cancer Report: Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention. IARC Press; 2020.
-
- Sarkozy C, Sehn LH. New drugs for the management of relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Lymphoma. 2019;3:310.
-
- Locke F, Miklos DB, Jacobson C, et al. . Primary analysis of ZUMA 7: a phase 3 randomized trial of axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) versus standard of care therapy in patients with relapsed/ refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2021;138(Suppl 1):2.
-
- Kamdar M, Solomon SR, Arnason J, et al. . Lisocabtagene maraleucel versus standard of care with salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation as second-line treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (TRANSFORM): results from an interim analysis. Lancet. 2022;399(10343):2294-2308. - PubMed

