Roles, outcomes, and enablers within research partnerships: A rapid review of the literature on patient and public involvement and engagement in health research
- PMID: 37322525
- PMCID: PMC10268359
- DOI: 10.1186/s40900-023-00448-z
Roles, outcomes, and enablers within research partnerships: A rapid review of the literature on patient and public involvement and engagement in health research
Abstract
Background: Recent studies mention a need to investigate partnership roles and dynamics within patient and public involvement and engagement (PPIE) in health research, and how impact and outcomes are achieved. Many labels exist to describe involvement processes, but it is unknown whether the label has implications on partnerships and outcomes. This rapid review investigates how roles between patients, relatives and researchers in a broad variety of PPIE activities in health research are described in peer reviewed papers and explores what enables these partnerships.
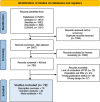
Methods: Rapid review of articles published between 2012 and February 2022 describing, evaluating, or reflecting on experiences of PPIE in health research. All research disciplines and research areas were eligible. Four databases (Medline, Embase, PsychInfo and CINAHL) were searched between November 2021 and February 2022. We followed PRISMA guidelines and extracted descriptive factors: year, origin, research area and discipline, study focus, framework used and co-authorship. On a selection of articles, we performed a narrative analysis of partnership roles using Smits et al.'s. Involvement Matrix. Lastly, we performed a meta synthesis of reported enablers and outcomes of the partnerships. Patients and Relatives (PRs) have been involved in the whole rapid review process and are co-authors of this article.
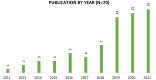
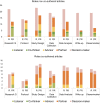
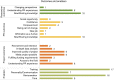
Results: Seventy articles from various research disciplines and areas were included. Forty articles were selected for a narrative analysis of the role description of PRs and researchers, and a meta synthesis of enablers and outcomes. Most articles described researchers as decision-makers throughout the research cycle. PRs most often were partners when they were included as co-authors; they were mostly partners in the design, analysis, write-up, and dissemination stages. Enablers of partnerships included: PR training, personality of PRs and communication skills, trust, remuneration and time.
Conclusions: Researchers' decision-making roles gives them control of where and when to include PRs in their projects. Co-authorship is a way of acknowledging patients' contributions which may lead to legitimation of their knowledge and the partnership. Authors describe common enablers, which can help future partnership formation.
Keywords: Co-authorship; Coproduction; Evaluation; Health research; Partnerships; Patient and public involvement; Rapid review.
Plain language summary
This article investigates how other articles describe the roles patients, relatives and researchers have in patient and public involvement activities in health research. It also investigates which factors are supportive of creating these research partnerships. We searched four health research databases and found 70 relevant articles which somehow evaluated patient involvement activities in research. From these 70 articles we chose 40 which we closely investigated for descriptions of roles in the partnerships between researchers and patients and relatives. For this, we used a tool called the Involvement Matrix which uses five different roles: Listener (who is given information), Co-thinker (who is asked to give opinion), Advisor (who gives (un)solicited advice), Partner (who works as an equal partner) and Decision-maker (Who takes initiative and (final) decisions). We found that it is often researchers who take on the role of Decision-maker and that involvement often happens on their terms. We noticed that patients and relatives most often had the role of partner, when they were listed as co-authors of the article. This shows co-authorship as an authorization of their work during patient and public involvement activities. We found that patient and relative training, patients’ and relatives’ personality and communication skills, trust, financial reimbursement, and time were mentioned most often as enablers of good research partnerships.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
A qualitative systematic review of internal and external influences on shared decision-making in all health care settings.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(58):4633-4646. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-432. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820528
-
Recognizing patient partner contributions to health research: a systematic review of reported practices.Res Involv Engagem. 2023 Sep 9;9(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s40900-023-00488-5. Res Involv Engagem. 2023. PMID: 37689741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conceptualising the initiation of researcher and research user partnerships: a meta-narrative review.Health Res Policy Syst. 2020 Feb 18;18(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12961-020-0536-9. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020. PMID: 32070367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An ethics framework for the transition to an operational learning healthcare system.Learn Health Syst. 2024 Mar 14;8(3):e10414. doi: 10.1002/lrh2.10414. eCollection 2024 Jul. Learn Health Syst. 2024. PMID: 39036527 Free PMC article.
-
From Innovator Result-driven to Multi-actor Impact-oriented Public-Private Partnerships: Integrating the Patient Perspective.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;286:137-168. doi: 10.1007/164_2024_730. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39235487 Review.
-
Enhancing Research Involvement of Young People With Lived Expertise: Reflecting on Experiences in Digital Mental Health Research.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Oct 18;26:e55441. doi: 10.2196/55441. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39423372 Free PMC article.
-
What motivates public collaborators to become and stay involved in health research?Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Feb 12;10(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00555-5. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 38347609 Free PMC article.
-
Conducting Patient-Oriented Research in Pediatric Populations: A Narrative Review.Children (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;11(10):1266. doi: 10.3390/children11101266. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457231 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Minogue V, Donskoy A-L. Developing a training package. Int J Health Care Qual Assur. 2017;30:458–466. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

