Combination of Enzymes with Materials to Give Them Antimicrobial Features: Modern Trends and Perspectives
- PMID: 36826863
- PMCID: PMC9960987
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14020064
Combination of Enzymes with Materials to Give Them Antimicrobial Features: Modern Trends and Perspectives
Abstract
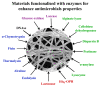
Multidrug-resistant bacteria form serious problems in many areas, including medicine and the food industry. At the same time, great interest is shown in the transfer or enhancement of antimicrobial properties to various materials by modifying them with enzymes. The use of enzymes in biomaterials with antimicrobial properties is important because enzymes can be used as the main active components providing antimicrobial properties of functionalized composite biomaterials, or can serve as enhancers of the antimicrobial action of certain substances (antibiotics, antimicrobial peptides, metal nanoparticles, etc.) against cells of various microorganisms. Enzymes can simultaneously widen the spectrum of antimicrobial activity of biomaterials. This review presents the most promising enzymes recently used for the production of antibacterial materials, namely hydrolases and oxidoreductases. Computer modeling plays an important role in finding the most effective combinations between enzymes and antimicrobial compounds, revealing their possible interactions. The range of materials that can be functionalized using enzymes looks diverse. The physicochemical characteristics and functionalization methods of the materials have a significant impact on the activity of enzymes. In this context, fibrous materials are of particular interest. The purpose of this review is to analyze the current state of the art in this area.
Keywords: antibiotics; antimicrobial peptides; biocompatibility; computational modeling; functionalized materials; hydrolyses; immobilization; lactonases; metal nanoparticles; oxidoreductases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Some Essential Oils-Present Status and Future Perspectives.Medicines (Basel). 2017 Aug 8;4(3):58. doi: 10.3390/medicines4030058. Medicines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28930272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of microbial biofilms - the contribution of micro and nanostructured materials.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(29):3311. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140304101314. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24606506
-
Application of Antimicrobial Peptides of the Innate Immune System in Combination With Conventional Antibiotics-A Novel Way to Combat Antibiotic Resistance?Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 30;9:128. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00128. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31114762 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-review: Antimicrobial peptides and enzymes as promising candidates to functionalize biomaterial surfaces.Biofouling. 2014;30(4):483-99. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2014.889120. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Biofouling. 2014. PMID: 24666008 Review.
-
Bacterial Cellulose Containing Combinations of Antimicrobial Peptides with Various QQ Enzymes as a Prototype of an "Enhanced Antibacterial" Dressing: In Silico and In Vitro Data.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Nov 27;12(12):1155. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12121155. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33261218 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
"Stop, Little Pot" as the Motto of Suppressive Management of Various Microbial Consortia.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 12;12(8):1650. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081650. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of Pt-MoS2 with enhanced photothermal and peroxidase-like properties and its antibacterial application.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 18;14(40):29428-29438. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05487c. eCollection 2024 Sep 12. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39297038 Free PMC article.
-
Double-Network Chitosan-Based Hydrogels with Improved Mechanical, Conductive, Antimicrobial, and Antibiofouling Properties.Gels. 2023 Mar 29;9(4):278. doi: 10.3390/gels9040278. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37102890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Various Biomimetics, Including Peptides as Antifungals.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Oct 28;8(7):513. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8070513. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ogunsona E.O., Muthuraj R., Ojogbo E., Valerio O., Mekonnen T.H. Engineered nanomaterials for antimicrobial applications: A review. Appl. Mater. Today. 2020;18:100473. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2019.100473. - DOI
-
- Wang Y., Yang Y., Shi Y., Song H., Yu C. Antibiotic-free antibacterial strategies enabled by nanomaterials: Progress and perspectives. Adv. Mater. 2020;32:1904106. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

