Integration of high-throughput omics technologies in medicinal plant research: The new era of natural drug discovery
- PMID: 36743502
- PMCID: PMC9891177
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1073848
Integration of high-throughput omics technologies in medicinal plant research: The new era of natural drug discovery
Abstract
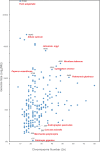
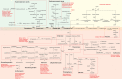
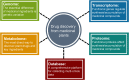
Medicinal plants are natural sources to unravel novel bioactive compounds to satisfy human pharmacological potentials. The world's demand for herbal medicines is increasing year by year; however, large-scale production of medicinal plants and their derivatives is still limited. The rapid development of modern technology has stimulated multi-omics research in medicinal plants, leading to a series of breakthroughs on key genes, metabolites, enzymes involved in biosynthesis and regulation of active compounds. Here, we summarize the latest research progress on the molecular intricacy of medicinal plants, including the comparison of genomics to demonstrate variation and evolution among species, the application of transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics to explore dynamic changes of molecular compounds, and the utilization of potential resources for natural drug discovery. These multi-omics research provide the theoretical basis for environmental adaptation of medicinal plants and allow us to understand the chemical diversity and composition of bioactive compounds. Many medicinal herbs' phytochemical constituents and their potential health benefits are not fully explored. Given their large diversity and global distribution as well as the impacts of growth duration and environmental factors on bioactive phytochemicals in medicinal plants, it is crucial to emphasize the research needs of using multi-omics technologies to address basic and applied problems in medicinal plants to aid in developing new and improved medicinal plant resources and discovering novel medicinal ingredients.
Keywords: active ingredients; biosynthesis pathways; high-throughput omics; medicinal plant; phytochemicals.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Zeng, Jiao, Ye, Li, Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
From single- to multi-omics: future research trends in medicinal plants.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Jan 19;24(1):bbac485. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac485. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 36416120 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated omics analysis of specialized metabolism in medicinal plants.Plant J. 2017 May;90(4):764-787. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13485. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28109168
-
The Current Developments in Medicinal Plant Genomics Enabled the Diversification of Secondary Metabolites' Biosynthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 14;23(24):15932. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415932. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Development of Plant Metabolomics and Medicinal Plant Genomics].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(1):1-18. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.17-00193. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 29311454 Review. Japanese.
-
[Systems biology applications to explore secondary metabolites in medicinal plants].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Jan;35(1):8-12. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20100101. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20349706 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Plant Metabolomics: The Future of Anticancer Drug Discovery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;17(10):1307. doi: 10.3390/ph17101307. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pelargonium graveolens: Towards In-Depth Metabolite Profiling, Antioxidant and Enzyme-Inhibitory Potential.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 19;13(18):2612. doi: 10.3390/plants13182612. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339589 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Climate Change and Mitigation Strategies for Some Abiotic and Biotic Constraints Influencing Fruit Growth and Quality.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;13(14):1942. doi: 10.3390/plants13141942. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An X., Luo X. H., Liu T. T., Li W. L., Zou L. N. (2022). Development and application of fruit color-related expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat markers in Abelmoschus esculentus on the basis of transcriptome sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.907895 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Awouafack M. D., Tane P., Kuete V., Eloff J. N. (2013). “2 - sesquiterpenes from the medicinal plants of Africa,” in Medicinal plant research in Africa. Ed. Kuete. V. (Oxford: Elsevier; ), 33–103.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

