Efficacy and Safety of Fezolinetant in Moderate to Severe Vasomotor Symptoms Associated With Menopause: A Phase 3 RCT
- PMID: 36734148
- PMCID: PMC10348473
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgad058
Efficacy and Safety of Fezolinetant in Moderate to Severe Vasomotor Symptoms Associated With Menopause: A Phase 3 RCT
Abstract
Context: Vasomotor symptoms (VMS) are common, bothersome, and can persist for years before and after menopause.
Objective: We aimed to assess efficacy/safety of fezolinetant for treatment of moderate to severe VMS associated with menopause.
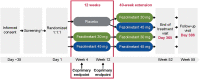
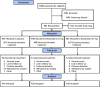
Methods: In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, 12-week phase 3 trial with a 40-week active treatment extension (NCT04003142; SKYLIGHT 2), women aged 40 to 65 years with minimum average 7 moderate to severe VMS/day were randomized to 12 weeks of once-daily placebo, fezolinetant 30 mg, or fezolinetant 45 mg. Completers were rerandomized to fezolinetant 30/45 mg for 40 additional weeks. Coprimary efficacy endpoints were mean daily change from baseline to week 4 (W4) and W12 in VMS frequency and severity. Safety was also assessed.
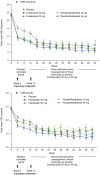
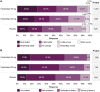
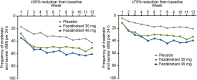
Results: Both fezolinetant doses statistically significantly reduced VMS frequency/severity at W4 and W12 vs placebo. For VMS frequency, W4 least squares mean (SE) reduction vs placebo: fezolinetant 30 mg, -1.82 (0.46; P < .001); 45 mg, -2.55 (0.46; P < .001); W12: 30 mg, -1.86 (0.55; P < .001); 45 mg, -2.53 (0.55; P < .001). For VMS severity, W4: 30 mg, -0.15 (0.06; P < .05); 45 mg, -0.29 (0.06; P < .001); W12: 30 mg, -0.16 (0.08; P < .05); 45 mg, -0.29 (0.08; P < .001). Improvement in VMS frequency and severity was observed by W1 and maintained through W52. Serious treatment-emergent adverse events were infrequent, reported by 2%, 1%, and 0% of those receiving fezolinetant 30 mg, fezolinetant 45 mg, and placebo, respectively.
Conclusion: Daily fezolinetant 30 and 45 mg were efficacious and well tolerated for treating moderate to severe VMS associated with menopause.
Keywords: KNDy; fezolinetant; neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist; nonhormonal; vasomotor symptoms.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Neurokinin Receptor Antagonist, Fezolinetant, for Treatment of Menopausal Vasomotor Symptoms.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Oct 18;108(11):e1448-e1449. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad209. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37097747 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant for moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause among women in East Asia: a phase 3 randomized study (MOONLIGHT I).J Int Med Res. 2024 May;52(5):3000605241247684. doi: 10.1177/03000605241247684. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38818888 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study.Lancet. 2023 Apr 1;401(10382):1091-1102. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00085-5. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Lancet. 2023. PMID: 36924778 Clinical Trial.
-
Fezolinetant treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause: effect of intrinsic and extrinsic factors in two phase 3 studies (SKYLIGHT 1 and 2).Menopause. 2024 Apr 1;31(4):247-257. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002340. Menopause. 2024. PMID: 38517210 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fezolinetant for the treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a meta-analysis.Climacteric. 2024 Jun;27(3):245-254. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2024.2334083. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Climacteric. 2024. PMID: 38619017 Review.
-
Fezolinetant: a novel nonhormonal therapy for vasomotor symptoms due to menopause.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024 Jun;25(9):1131-1136. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2024.2375039. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38953697 Review.
Cited by
-
Migraines, vasomotor symptoms, and cardiovascular disease in the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults study.Menopause. 2024 Mar 1;31(3):202-208. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000002311. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Menopause. 2024. PMID: 38350045 Free PMC article.
-
Brazilian Guideline on Menopausal Cardiovascular Health - 2024.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024 Aug 16;121(7):e20240478. doi: 10.36660/abc.20240478. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39166619 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
-
Psychometric evaluation of the PROMIS SD-SF-8b instrument in individuals experiencing vasomotor symptoms due to menopause.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2023 Nov 21;21(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12955-023-02206-x. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2023. PMID: 37990323 Free PMC article.
-
"Veozah (Fezolinetant): A Promising Non-Hormonal Treatment for Vasomotor Symptoms in Menopause".Health Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 5;6(10):e1610. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1610. eCollection 2023 Oct. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37808928 Free PMC article.
-
Oral micronized progesterone for perimenopausal night sweats and hot flushes a Phase III Canada-wide randomized placebo-controlled 4 month trial.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 5;13(1):9082. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35826-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37277418 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Rance NE, Dacks PA, Mittelman-Smith MA, Romanovsky AA, Krajewski-Hall SJ. Modulation of body temperature and LH secretion by hypothalamic KNDy (kisspeptin, neurokinin B and dynorphin) neurons: a novel hypothesis on the mechanism of hot flushes. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2013;34(3):211‐227. - PMC - PubMed

