Production of rhamnolipid biosurfactants in solid-state fermentation: process optimization and characterization studies
- PMID: 36694155
- PMCID: PMC9872355
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-022-00772-4
Production of rhamnolipid biosurfactants in solid-state fermentation: process optimization and characterization studies
Abstract
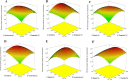
Background: Rhamnolipids are a group of the extracellular microbial surface-active molecules produced by certain Pseudomonas species with various environmental and industrial applications. The goal of the present research was to identify and optimize key process parameters for Pseudomonas aeruginosa PTCC 1074s synthesis of rhamnolipids utilizing soybean meal in solid state fermentation. A fractional factorial design was used to screen the key nutritional and environmental parameters to achieve the high rhamnolipid production. Response surface methodology was used to optimize the levels of four significant factors.
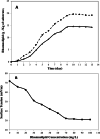
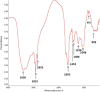
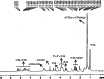
Results: The characterization of biosurfactant by TLC, FT-IR and H-NMR showed the rhamnolipids presence. In the optimum conditions (temperature 34.5 °C, humidity 80%, inoculum size 1.4 mL, and glycerol 5%), the experimental value of rhamnolipid production was 19.68 g/kg dry substrate. The obtained rhamnolipid biosurfactant decreased water's surface tension from 71.8 ± 0.4 to 32.2 ± 0.2 mN/m with a critical micelle concentration of nearly 70 mg/L. Additionally, analysis of the emulsification activity revealed that the generated biosurfactant was stable throughout a broad pH, temperature, and NaCl concentration range.
Conclusions: The current study confirmed the considerable potential of agro-industrial residues in the production of rhamnolipid and enhanced the production yield by screening and optimizing the significant process parameters.
Keywords: Agro-industrial residues; Biosurfactant; Optimization; Response surface methodology; Solid-state fermentation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microbial conversion of agro-processing waste (peanut meal) to rhamnolipid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: solid-state fermentation, water extraction, medium optimization and potential applications.Bioresour Technol. 2023 Feb;369:128426. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128426. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Bioresour Technol. 2023. PMID: 36462764
-
Designer rhamnolipids by reduction of congener diversity: production and characterization.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Dec 14;16(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0838-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 29241456 Free PMC article.
-
Biosurfactant production from novel air isolate NITT6L: screening, characterization and optimization of media.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Sep 28;23(9):1229-43. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1212.12031. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23851275
-
Recent progress towards industrial rhamnolipids fermentation: Process optimization and foam control.Bioresour Technol. 2020 Feb;298:122394. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122394. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Bioresour Technol. 2020. PMID: 31757615 Review.
-
Rhamnolipid biosurfactants: evolutionary implications, applications and future prospects from untapped marine resource.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2016;36(3):399-415. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2014.979758. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 25641324 Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the potential of biosurfactants: Innovations in metabolic and genetic engineering for sustainable industrial and environmental solutions.Biotechnol Notes. 2024 Jul 25;5:111-119. doi: 10.1016/j.biotno.2024.07.001. eCollection 2024. Biotechnol Notes. 2024. PMID: 39416688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Insights into Cr(VI)-Induced Rhamnolipid Production and Gene Expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa RW9 for Potential Bioremediation.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 28;34(9):1877-1889. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2406.06034. Epub 2024 Jul 19. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39343606 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-control of soil-borne virus infection by seed application of Glycyrrhiza glabra extract and the rhamnolipid Rhapynal.Planta. 2024 Sep 13;260(4):94. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04529-5. Planta. 2024. PMID: 39269658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chandrasekaran EV, BeMiller JN, Song-Chiau DL. Isolation, partial characterization, and biological properties of polysaccharides from crude papain. Carbohydr Res. 1987;860:105–115. - PubMed
-
- Saharan BS, Sahu RK, Sharma D. A review on biosurfactants: fermentation. Current developments and perspectives. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2011;29:1–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

