Glasius bio-inspired neural networks based UV-C disinfection path planning improved by preventive deadlock processing algorithm
- PMID: 36465142
- PMCID: PMC9695870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2022.103330
Glasius bio-inspired neural networks based UV-C disinfection path planning improved by preventive deadlock processing algorithm
Abstract
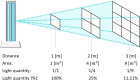
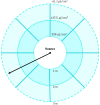
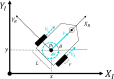
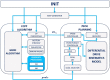
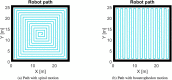
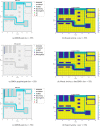
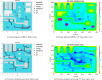
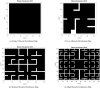
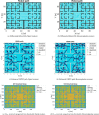
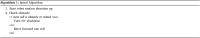
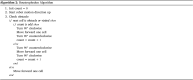
The COVID-19 pandemic made robot manufacturers explore the idea of combining mobile robotics with UV-C light to automate the disinfection processes. But performing this process in an optimum way introduces some challenges: on the one hand, it is necessary to guarantee that all surfaces receive the radiation level to ensure the disinfection; at the same time, it is necessary to minimize the radiation dose to avoid the damage of the environment. In this work, both challenges are addressed with the design of a complete coverage path planning (CCPP) algorithm. To do it, a novel architecture that combines the glasius bio-inspired neural network (GBNN), a motion strategy, an UV-C estimator, a speed controller, and a pure pursuit controller have been designed. One of the main issues in CCPP is the deadlocks. In this application they may cause a loss of the operation, lack of regularity and high peaks in the radiation dose map, and in the worst case, they can make the robot to get stuck and not complete the disinfection process. To tackle this problem, in this work we propose a preventive deadlock processing algorithm (PDPA) and an escape route generator algorithm (ERGA). Simulation results show how the application of PDPA and the ERGA allow to complete complex maps in an efficient way where the application of GBNN is not enough. Indeed, a 58% more of covered surface is observed. Furthermore, two different motion strategies have been compared: boustrophedon and spiral motion, to check its influence on the performance of the robot navigation.
Keywords: Complete coverage path planning; Deadlocks; Escape routes; Mobile robot; UV-C.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a Hybrid Path Planning Algorithm and a Bio-Inspired Control for an Omni-Wheel Mobile Robot.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jul 30;20(15):4258. doi: 10.3390/s20154258. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751685 Free PMC article.
-
Coverage Planning for UVC Irradiation: Robot Surface Disinfection Based on Swarm Intelligence Algorithm.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 26;24(11):3418. doi: 10.3390/s24113418. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894209 Free PMC article.
-
Biologically Inspired Complete Coverage Path Planning Algorithm Based on Q-Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 May 11;23(10):4647. doi: 10.3390/s23104647. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37430561 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-Inspired Optimization-Based Path Planning Algorithms in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: A Survey.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 12;23(6):3051. doi: 10.3390/s23063051. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36991762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An efficient neural network approach to dynamic robot motion planning.Neural Netw. 2000 Mar;13(2):143-8. doi: 10.1016/s0893-6080(99)00103-3. Neural Netw. 2000. PMID: 10935758 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved RRT* Algorithm for Disinfecting Robot Path Planning.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;24(5):1520. doi: 10.3390/s24051520. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization W.H., et al. 2020. Cleaning and disinfection of environmental surfaces in the context of COVID-19.
-
- 2022. Disinfection robot market. https://www.persistencemarketresearch.com/market-research/disinfection-r.... [Accessed 13 July 2022]
-
- Sierra Garcia J., Guillen-Grima F., Garcia-Garcia M., Cascajar L., Rodriguez-Merino F. Evaluation of an UVC robot for terminal disinfection of hospital rooms. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021
-
- Mitxelena-Iribarren O., Mondragon B., Pérez-Lorenzo E., Smerdou C., Guillen-Grima F., Sierra-Garcia J.E., et al. Evaluation of the degradation of materials by exposure to germicide UV-C light through colorimetry, tensile strength and surface microstructure analyses. Mater Today Commun. 2022
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
