Nutraceuticals for Complementary Treatment of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Perspective from Their Use in COVID-19
- PMID: 36295088
- PMCID: PMC9605437
- DOI: 10.3390/life12101652
Nutraceuticals for Complementary Treatment of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Perspective from Their Use in COVID-19
Abstract
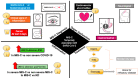
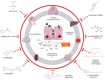
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) has been widely reported in some children diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2. Clinical signs of MIS-C are manifested at 2 to 4 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection, where elevated biomarkers of inflammation and cardiac dysfunction are the hallmark of this syndrome when infection or exposure to SARS-CoV-2 has been confirmed. However, after two years of acknowledgment, MIS-C treatment is still under research to reach safety and effectiveness in the acute phase in children. Therefore, in this review, we discuss the potential use of natural compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects to reduce collateral damage caused by hyperinflammation in MIS-C pathology for new research in treatment and interventions.
Keywords: children; multisystem inflammatory syndrome; nutraceutical compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in neonates (MIS-N) associated with SARS-CoV2 infection: a case series.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 May;181(5):1883-1898. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04377-z. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35031848 Free PMC article.
-
Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022 May;22(5):53-60. doi: 10.1007/s11882-022-01031-4. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022. PMID: 35314921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 in children and adolescents: from COVID-19 pneumonia to multisystem inflammatory syndrome: a multicentre study in pediatric intensive care units in Spain.Crit Care. 2020 Nov 26;24(1):666. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03332-4. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 33243303 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibody Release in Children after Corona Virus mRNA Vaccination: A Risk Factor of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome?Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;9(11):1353. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9111353. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835284 Free PMC article.
-
Severe COVID-19, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease: immunological mechanisms, clinical manifestations and management.Rheumatol Int. 2021 Jan;41(1):19-32. doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04749-4. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 33219837 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Vitamin D Levels on Clinical Manifestations of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Cross-Sectional Study.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;13(3):674. doi: 10.3390/life13030674. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castagnoli R., Votto M., Licari A., Brambilla I., Bruno R., Perlini S., Rovida F., Baldanti F., Marseglia G.L. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. JAMA Pediatr. 2020;174:882–889. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1467. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pouletty M., Borocco C., Ouldali N., Caseris M., Basmaci R., Lachaume N., Bensaid P., Pichard S., Kouider H., Morelle G., et al. Paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 mimicking Kawasaki disease (Kawa-COVID-19): A multicentre cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020;79:999–1006. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217960. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramcharan T., Nolan O., Lai C.Y., Prabhu N., Krishnamurthy R., Richter A.G., Jyothish D., Kanthimathinathan H.K., Welch S.B., Hackett S., et al. Paediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome: Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS): Cardiac Features, Management and Short-Term Outcomes at a UK Tertiary Paediatric Hospital. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2020;41:1391–1401. doi: 10.1007/s00246-020-02391-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Toubiana J., Poirault C., Corsia A., Bajolle F., Fourgeaud J., Angoulvant F., Debray A., Basmaci R., Salvador E., Biscardi S., et al. Kawasaki-like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children during the COVID-19 pandemic in Paris, France: Prospective observational study. BMJ. 2020;369:m2094. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2094. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whittaker E., Bamford A., Kenny J., Kaforou M., Jones C., Shah P., Ramnarayan P., Fraisse A., Miller O., Davies P., et al. Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children with a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2. JAMA. 2020;324:259–269. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.10369. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

