Complete Genome Sequences of One Salt-Tolerant and Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Emulsifying Terribacillus saccharophilus Strain ZY-1
- PMID: 35966672
- PMCID: PMC9366552
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.932269
Complete Genome Sequences of One Salt-Tolerant and Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Emulsifying Terribacillus saccharophilus Strain ZY-1
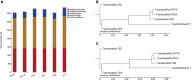
Abstract
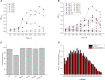
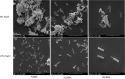
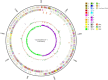
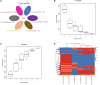
Salt tolerance is one of the most important problems in the field of environmental governance and restoration. Among the various sources of factors, except temperature, salinity is a key factor that interrupts bacterial growth significantly. In this regard, constant efforts are made for the development of salt-tolerant strains, but few strains with salt tolerance, such as Terribacillus saccharophilus, were found, and there are still few relevant reports about their salt tolerance from complete genomic analysis. Furthermore, with the development of the economy, environmental pollution caused by oil exploitation has attracted much attention, so it is crucial to find the bacteria from T. saccharophilus which could degrade petroleum hydrocarbon even under high-salt conditions. Herein, one T. saccharophilus strain named ZY-1 with salt tolerance was isolated by increasing the salinity on LB medium step by step with reservoir water as the bacterial source. Its complete genome was sequenced, which was the first report of the complete genome for T. saccharophilus species with petroleum hydrocarbon degradation and emulsifying properties. In addition, its genome sequences were compared with the other five strains that are from the same genus level. The results indicated that there really exist some differences among them. In addition, some characteristics were studied. The salt-tolerant strain ZY-1 developed in this study and its emulsification and degradation performance of petroleum hydrocarbons were studied, which is expected to widely broaden the research scope of petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria in the oil field environment even in the extreme environment. The experiments verified that ZY-1 could significantly grow not only in the salt field but also in the oil field environment. It also demonstrated that the developed salt-tolerant strain can be applied in the petroleum hydrocarbon pollution field for bioremediation. In addition, we expect that the identified variants which occurred specifically in the high-salt strain will enhance the molecular biological understanding and be broadly applied to the biological engineering field.
Keywords: Terribacillus saccharophilus; comparative genomics; complete genome; salt-tolerant; strain ZY-1.
Copyright © 2022 Su, Yang, Li, Chen, Wang, Yun, Li and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic and Comparative Genome Analysis of Exiguobacterium aurantiacum SW-20, a Petroleum-Degrading Bacteria with Salt Tolerance and Heavy Metal-Tolerance Isolated from Produced Water of Changqing Oilfield, China.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 29;10(1):66. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010066. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 35056515 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of Halomonas sp. strain C2SS100, a hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium under hypersaline conditions.J Appl Microbiol. 2009 Sep;107(3):785-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04251.x. Epub 2009 Mar 23. J Appl Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19320948
-
Genomic characterization of Enterobacter xiangfangensis STP-3: Application to real time petroleum oil sludge bioremediation.Microbiol Res. 2021 Dec;253:126882. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2021.126882. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Microbiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34619415
-
[Advances in biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021 Aug 25;37(8):2765-2778. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200611. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34472294 Review. Chinese.
-
Recent studies in microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in hypersaline environments.Front Microbiol. 2014 Apr 23;5:173. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00173. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24795705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ash C., Farrow A. J. E., Wallbanks S., Collins M. D. (1991). Phylogenetic heterogeneity of the genus Bacillus revealed by comparative analysis of small-subunit-ribosomal RNA sequences. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 13 202–206.
-
- Banat I. M., Rienzo M. D., Quinn G. A. (2014). Microbial biofilms: biosurfactants as antibiofilm agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98 9915–9929. - PubMed
-
- Claus D., Berkeley R. (1986). Genus Bacillus Cohn 1872. Bergey Man. Syst. Bacteriol. 2 27–32.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

