Xeroderma pigmentosum: an updated review
- PMID: 35520754
- PMCID: PMC9045481
- DOI: 10.7573/dic.2022-2-5
Xeroderma pigmentosum: an updated review
Abstract
Background: Early recognition of xeroderma pigmentosum is important to minimize the complications arising from the harmful effects of exposure to ultraviolet radiation. This narrative review aims to familiarize physicians with the clinical features, diagnosis and management of xeroderma pigmentosum.
Methods: A search was conducted in December 2021 in PubMed Clinical Queries using the key term "xeroderma pigmentosum". The search strategy included all clinical trials, observational studies and reviews published within the past 10 years. The information retrieved from the search was used in the compilation of this article.
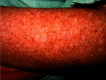
Results: Xeroderma pigmentosum is a condition of abnormal DNA repair of ultraviolet radiation-induced and oxidative DNA damage, which leads to increased skin cancer susceptibility. Approximately 50% of patients with xeroderma pigmentosum have increased photosensitivity and certain types of xeroderma pigmentosum are more prone to ocular disease and progressive neurodegeneration depending on the causative mutation. The diagnosis should be suspected in patients with increased photosensitivity and characteristic cutaneous, ophthalmological and neurological findings. A definite diagnosis can be made by the identification of biallelic mutation in one of the causative genes. Strict and consistent sun avoidance and protection and early detection and treatment of premalignant and malignant skin lesions are the mainstays of management. Treatment options for actinic keratosis include cryotherapy, topical imiquimod, topical 5-fluorouracil, chemical peeling, excision, CO2 laser resurfacing, fractional/pulsed laser therapy, and photodynamic therapy. Cutaneous malignancy can be treated by photodynamic therapy, curettage and electrodesiccation, or surgical excision. Oral isotretinoin, oral niacinamide, topical imiquimod and topical fluorouracil can be used for the prevention of skin malignancy. Treatment options for poikiloderma include chemical peeling, dermabrasion and laser resurfacing. Methylcellulose eyedrops and soft ultraviolet-protective contact lenses may be used to keep the cornea moist and protect against the harmful effects of keratitis sicca. Investigational therapies include the use of T4 endonuclease-V liposome lotion and oral nicotinamide to reduce the rate of actinic keratoses and non-melanoma skin cancers and gene therapy for radical cure of this condition.
Conclusion: Although currently there is no cure for xeroderma pigmentosum, increased awareness and early diagnosis of the condition, followed by rigorous sun avoidance and protection and optimal management, can dramatically improve the quality of life and life expectancy.
Keywords: conjunctival injection; conjunctival neovascularization; neurodegeneration; photophobia; poikiloderma; skin cancers; xeroderma pigmentosum.
Copyright © 2022 Leung AKC, Barankin B, Lam JM, Leong KF, Hon KL.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and potential conflicts of interest: AKCL and KLH are associate editors of Drugs in Context and confirm that this article has no other conflicts of interest otherwise. This manuscript was sent out for independent peer review. The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) Potential Conflicts of Interests form for the authors is available for download at: https://www.drugsincontext.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/dic.2022-2-5-COI.pdf
Figures






Similar articles
-
Effect of topically applied T4 endonuclease V in liposomes on skin cancer in xeroderma pigmentosum: a randomised study. Xeroderma Pigmentosum Study Group.Lancet. 2001 Mar 24;357(9260):926-9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)04214-8. Lancet. 2001. PMID: 11289350 Clinical Trial.
-
Xeroderma Pigmentosum: Novel Prophylactic and Therapeutic Approaches. Part One: Topical Zinc Sulfate 25% and Heat Dermabrasion plus Topical Trichloroacetic Acid.Skinmed. 2023 Nov 10;21(5):330-335. eCollection 2023. Skinmed. 2023. PMID: 37945358
-
Xeroderma pigmentosum and its dental implications.Eur J Dent. 2015 Jan-Mar;9(1):145-148. doi: 10.4103/1305-7456.149664. Eur J Dent. 2015. PMID: 25713498 Free PMC article.
-
Novel therapeutic approaches to xeroderma pigmentosum.Br J Dermatol. 2019 Aug;181(2):249-255. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17253. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Br J Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30265743 Review.
-
Xeroderma pigmentosum: a case report and review of the literature.J Prev Med Hyg. 2010 Jun;51(2):87-91. J Prev Med Hyg. 2010. PMID: 21155411 Review.
Cited by
-
Xeroderma Pigmentosum with a Rapidly Proliferating Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a 4-Year Old Kid: A Rare Entity in Indian Subcontinent.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2024 Aug;23(4):990-993. doi: 10.1007/s12663-024-02269-3. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2024. PMID: 39118905
-
Single-mitosis dissection of acute and chronic DNA mutagenesis and repair.Nat Genet. 2024 May;56(5):913-924. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01712-y. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 38627597 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Exome Sequencing of a Patient with a Milder Phenotype of Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group C.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 3;59(4):699. doi: 10.3390/medicina59040699. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37109656 Free PMC article.
-
SNP Array Screening and Long Range PCR-Based Targeted Next Generation Sequencing for Autosomal Recessive Disease with Consanguinity: Insight from a Case of Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group C.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 15;14(11):2079. doi: 10.3390/genes14112079. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003022 Free PMC article.
-
"Immunopeeling" Using Imiquimod for Xeroderma Pigmentosum.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2023 Nov 24;15(4):673-674. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_446_23. eCollection 2024 Jul-Aug. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2023. PMID: 39050050 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hebra F, Kaposi M. On diseases of the skin including exanthemata. Volume III. New Sydenham Soc. 1874;61:252–258.
-
- Eichenfield LF, Warner CG. Corona R, editor. Xeroderma pigmentosum. UpToDate. [Accessed 30 December 2021]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/xeroderma-pigmentosum .
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

