Bioprospecting Kluyveromyces marxianus as a Robust Host for Industrial Biotechnology
- PMID: 35519613
- PMCID: PMC9065261
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.851768
Bioprospecting Kluyveromyces marxianus as a Robust Host for Industrial Biotechnology
Abstract
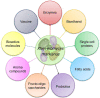
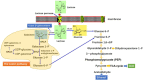
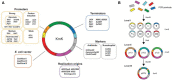
Kluyveromyces marxianus is an emerging non-conventional food-grade yeast that is generally isolated from diverse habitats, like kefir grain, fermented dairy products, sugar industry sewage, plants, and sisal leaves. A unique set of beneficial traits, such as fastest growth, thermotolerance, and broad substrate spectrum (i.e., hemi-cellulose hydrolysates, xylose, l-arabinose, d-mannose, galactose, maltose, sugar syrup molasses, cellobiose, and dairy industry) makes this yeast a particularly attractive host for applications in a variety of food and biotechnology industries. In contrast to Saccharomyces cerevisiae, most of the K. marxianus strains are apparently Crabtree-negative or having aerobic-respiring characteristics, and unlikely to endure aerobic alcoholic fermentation. This is a desirable phenotype for the large-scale biosynthesis of products associated with biomass formation because the formation of ethanol as an undesirable byproduct can be evaded under aerobic conditions. Herein, we discuss the current insight into the potential applications of K. marxianus as a robust yeast cell factory to produce various industrially pertinent enzymes, bioethanol, cell proteins, probiotic, fructose, and fructo-oligosaccharides, and vaccines, with excellent natural features. Moreover, the biotechnological improvement and development of new biotechnological tools, particularly CRISPR-Cas9-assisted precise genome editing in K. marxianus are delineated. Lastly, the ongoing challenges, concluding remarks, and future prospects for expanding the scope of K. marxianus utilization in modern biotechnology, food, feed, and pharmaceutical industries are also thoroughly vetted. In conclusion, it is critical to apprehend knowledge gaps around genes, metabolic pathways, key enzymes, and regulation for gaining a complete insight into the mechanism for producing relevant metabolites by K. marxianus.
Keywords: Kluyveromyces marxianus; bioethanol; enzymes; food; genome editing.
Copyright © 2022 Bilal, Ji, Xu, Xu, Lin, Iqbal and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kluyveromyces marxianus: An emerging yeast cell factory for applications in food and biotechnology.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Nov 16;333:108818. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108818. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32805574 Review.
-
Engineering Kluyveromyces marxianus as a Robust Synthetic Biology Platform Host.mBio. 2018 Sep 25;9(5):e01410-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01410-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30254120 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and analysis of a Kluyveromyces marxianus genome-scale metabolic model.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Nov 6;20(1):551. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3134-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31694544 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of comprehensive data and biotechnological tools for industrial applications of Kluyveromyces marxianus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jan;104(2):475-488. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10224-3. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31781815 Review.
-
Kluyveromyces marxianus: a potential biocatalyst of renewable chemicals and lignocellulosic ethanol production.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2021 Dec;41(8):1131-1152. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1917505. Epub 2021 May 2. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33938342 Review.
Cited by
-
High-Yield Expressed Human Ferritin Heavy-Chain Nanoparticles in K. marxianus for Functional Food Development.Foods. 2024 Sep 15;13(18):2919. doi: 10.3390/foods13182919. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39335848 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of broad-host expression promoters for shuttle expression vectors in non-conventional yeasts and bacteria.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Aug 16;23(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02506-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39152436 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPRi-induced transcriptional regulation of IAH1 gene and its influence on volatile compounds profile in Kluyveromyces marxianus DU3.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 5;40(4):121. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03811-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38441729
-
Metabolic Engineering of Model Microorganisms for the Production of Xanthophyll.Microorganisms. 2023 May 9;11(5):1252. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051252. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges and prospects of microbial α-amylases for industrial application: a review.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 20;40(2):44. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03821-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38114825 Review.
References
-
- Alimardani-Theuil P., Gainvors-Claisse A., Duchiron F. (2011). Yeasts: An Attractive Source of Pectinases-From Gene Expression to Potential Applications: A Review. Process Biochem. 46 (8), 1525–1537. 10.1016/j.procbio.2011.05.010 - DOI
-
- Alonso-Vargas M., Téllez-Jurado A., Gómez-Aldapa C. A., Ramírez-Vargas M. D. R., Conde-Báez L., Castro-Rosas J., et al. (2022). Optimization of 2-Phenylethanol Production from Sweet Whey Fermentation Using Kluyveromyces Marxianus. Fermentation 8 (2), 39. 10.3390/fermentation8020039 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

