Recent Advances in the Development of Toll-like Receptor Agonist-Based Vaccine Adjuvants for Infectious Diseases
- PMID: 35214155
- PMCID: PMC8878135
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020423
Recent Advances in the Development of Toll-like Receptor Agonist-Based Vaccine Adjuvants for Infectious Diseases
Abstract
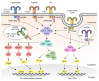
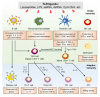
Vaccines are powerful tools for controlling microbial infections and preventing epidemic diseases. Efficient inactive, subunit, or viral-like particle vaccines usually rely on a safe and potent adjuvant to boost the immune response to the antigen. After a slow start, over the last decade there has been increased developments on adjuvants for human vaccines. The development of adjuvants has paralleled our increased understanding of the molecular mechanisms for the pattern recognition receptor (PRR)-mediated activation of immune responses. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a group of PRRs that recognize microbial pathogens to initiate a host's response to infection. Activation of TLRs triggers potent and immediate innate immune responses, which leads to subsequent adaptive immune responses. Therefore, these TLRs are ideal targets for the development of effective adjuvants. To date, TLR agonists such as monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) and CpG-1018 have been formulated in licensed vaccines for their adjuvant activity, and other TLR agonists are being developed for this purpose. The COVID-19 pandemic has also accelerated clinical research of vaccines containing TLR agonist-based adjuvants. In this paper, we reviewed the agonists for TLR activation and the molecular mechanisms associated with the adjuvants' effects on TLR activation, emphasizing recent advances in the development of TLR agonist-based vaccine adjuvants for infectious diseases.
Keywords: adjuvant; mRNA vaccine; nasal adjuvant; toll-like receptor; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor agonists as cancer vaccine adjuvants.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2297453. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2297453. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38155525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of Pattern Recognition Receptor Agonists as Candidate Adjuvants.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 6;11:745016. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.745016. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34692565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Protein Toll-Like-Receptor Agonists: A Novel Perspective on Vaccine Adjuvants.Front Immunol. 2019 May 29;10:1144. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01144. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31191528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists as a driving force behind next-generation vaccine adjuvants and cancer therapeutics.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Oct;70:102172. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102172. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35785601 Review.
-
Immune Adjuvant Effect of Molecularly-defined Toll-Like Receptor Ligands.Vaccines (Basel). 2014 Apr 25;2(2):323-53. doi: 10.3390/vaccines2020323. Vaccines (Basel). 2014. PMID: 26344622 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gaston Ramon's Big Four.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Jan 9;16(1):33. doi: 10.3390/toxins16010033. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38251249 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of Chemokines Receptors, Toll-like Receptors, and Host Immunological Pathways.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 25;11(9):2384. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092384. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and efficacy of toll-like receptor agonists as therapeutic agents and vaccine adjuvants for infectious diseases in animals: a systematic review.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 17;11:1428713. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1428713. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39355141 Free PMC article.
-
E6020, a TLR4 Agonist Adjuvant, Enhances Both Antibody Titers and Isotype Switching in Response to Immunization with Hapten-Protein Antigens and Is Diminished in Mice with TLR4 Signaling Insufficiency.J Immunol. 2022 Nov 15;209(10):1950-1959. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200495. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36426935 Free PMC article.
-
An mRNA vaccine for pancreatic cancer designed by applying in silico immunoinformatics and reverse vaccinology approaches.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 8;19(7):e0305413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305413. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38976715 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

