An Efficient Coalescent Epoch Model for Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference
- PMID: 35212733
- PMCID: PMC9773037
- DOI: 10.1093/sysbio/syac015
An Efficient Coalescent Epoch Model for Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference
Abstract
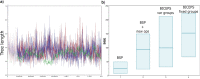
We present a two-headed approach called Bayesian Integrated Coalescent Epoch PlotS (BICEPS) for efficient inference of coalescent epoch models. Firstly, we integrate out population size parameters, and secondly, we introduce a set of more powerful Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) proposals for flexing and stretching trees. Even though population sizes are integrated out and not explicitly sampled through MCMC, we are still able to generate samples from the population size posteriors. This allows demographic reconstruction through time and estimating the timing and magnitude of population bottlenecks and full population histories. Altogether, BICEPS can be considered a more muscular version of the popular Bayesian skyline model. We demonstrate its power and correctness by a well-calibrated simulation study. Furthermore, we demonstrate with an application to SARS-CoV-2 genomic data that some analyses that have trouble converging with the traditional Bayesian skyline prior and standard MCMC proposals can do well with the BICEPS approach. BICEPS is available as open-source package for BEAST 2 under GPL license and has a user-friendly graphical user interface.[Bayesian phylogenetics; BEAST 2; BICEPS; coalescent model.].
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Systematic Biologists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Scalable Bayesian phylogenetics.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;377(1861):20210242. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0242. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35989603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
StarBeast3: Adaptive Parallelized Bayesian Inference under the Multispecies Coalescent.Syst Biol. 2022 Jun 16;71(4):901-916. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syac010. Syst Biol. 2022. PMID: 35176772 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Aug;29(8):1969-73. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss075. Epub 2012 Feb 25. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22367748 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7.Syst Biol. 2018 Sep 1;67(5):901-904. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syy032. Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29718447 Free PMC article.
-
A biologist's guide to Bayesian phylogenetic analysis.Nat Ecol Evol. 2017 Oct;1(10):1446-1454. doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0280-x. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Nat Ecol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28983516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AARS Online: A collaborative database on the structure, function, and evolution of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.IUBMB Life. 2024 Dec;76(12):1091-1105. doi: 10.1002/iub.2911. Epub 2024 Sep 9. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 39247978 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic epidemiology of Delta SARS-CoV-2 during transition from elimination to suppression in Aotearoa New Zealand.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 12;13(1):4035. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31784-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35821124 Free PMC article.
-
Purifying selection decreases the potential for Bangui orthobunyavirus outbreaks in humans.Virus Evol. 2023 Mar 8;9(1):vead018. doi: 10.1093/ve/vead018. eCollection 2023. Virus Evol. 2023. PMID: 37025159 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 variants during the first two years of the pandemic in Colombia.Commun Med (Lond). 2023 Jul 13;3(1):97. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00328-3. Commun Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37443390 Free PMC article.
-
Model design for nonparametric phylodynamic inference and applications to pathogen surveillance.Virus Evol. 2023 May 5;9(1):vead028. doi: 10.1093/ve/vead028. eCollection 2023. Virus Evol. 2023. PMID: 37229349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldous D.J. 2001. Stochastic models and descriptive statistics for phylogenetic trees, from Yule to today. Stat. Sci. 16(1):23–34.
-
- Bouckaert R., Vaughan T.G., Barido-Sottani J., Duchêne S., Fourment M., Gavryushkina A., Heled J., Jones G., Kühnert D., De Maio N., Matschiner M., Mendes F., Müller N., Ogilvie H., du Plessis L., Popinga A., Rambaut A., Rasmussen D., Siveroni I., Suchard M., Wu C.-H., Xie D., Zhang C., Stadler T., Drummond A.. 2019. BEAST 2.5: an advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15(1):e1006650. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campos P.F., Willerslev E., Sher A., Orlando L., Axelsson E., Tikhonov A., Aaris-S⊘rensen K., Greenwood A.D., Kahlke R.-D., Kosintsev P., et al.2010. Ancient DNA analyses exclude humans as the driving force behind late Pleistocene musk ox (Ovibos moschatus) population dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107(1):5675–5680. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

