Complete Relief of Painful Tonic Seizures in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder by Satralizumab Treatment
- PMID: 35135926
- PMCID: PMC9556229
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9036-21
Complete Relief of Painful Tonic Seizures in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder by Satralizumab Treatment
Abstract
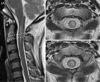
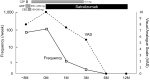
Satralizumab, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-6 receptors, has been approved for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD). Several reports have described the effectiveness of satralizumab against neuropathic pain in patients with NMOSD, but its effects on painful tonic seizures have not yet been reported. We herein report a Japanese woman with anti-aquaporin-4 antibody-positive NMOSD whose painful tonic seizures completely resolved after six months of satralizumab treatment. In conclusion, interleukin-6 blocking may be effective against painful tonic seizures. This effect may be due to suppression of microglial activation and the resultant neuronal hyperexcitability.
Keywords: IL-6; neuromyelitis optica; painful tonic seizures; satralizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Satralizumab: A Review in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder.CNS Drugs. 2023 Apr;37(4):363-370. doi: 10.1007/s40263-023-00995-9. Epub 2023 Mar 18. CNS Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36933107 Review.
-
[Local experience of IL-6 pathway inhibition with satralizumab for patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2022;122(7. Vyp. 2):68-72. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202212207268. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2022. PMID: 35912559 Russian.
-
Severe febrile neutropenia associated with satralizumab in an Argentinian neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder patient.Mult Scler. 2023 Jan;29(1):150-153. doi: 10.1177/13524585221137231. Epub 2022 Nov 27. Mult Scler. 2023. PMID: 36437566
-
Trial of Satralizumab in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder.N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 28;381(22):2114-2124. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1901747. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31774956 Clinical Trial.
-
Satralizumab: First Approval.Drugs. 2020 Sep;80(14):1477-1482. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01380-2. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32797372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-IL-6 therapies in central nervous system inflammatory demyelinating diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:966766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.966766. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uzawa A, Mori M, Arai K, et al. . Cytokine and chemokine profiles in neuromyelitis optica: significance of interleukin-6. Mult Scler 16: 1443-1452, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Uchida T, Mori M, Uzawa A, et al. . Increased cerebrospinal fluid metalloproteinase-2 and interleukin-6 are associated with albumin quotient in neuromyelitis optica: their possible role on blood-brain barrier disruption. Mult Scler 23: 1072-1084, 2017. - PubMed

