Impact of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation on new silicone half-piece elastometric respirator (VJR-NMU) performance, structural integrity and sterility during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 34648544
- PMCID: PMC8516203
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258245
Impact of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation on new silicone half-piece elastometric respirator (VJR-NMU) performance, structural integrity and sterility during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
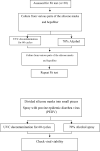
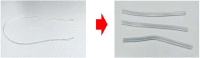
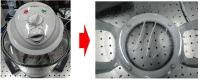
Since the innovation of our new half-piece elastometric respirator, this type of filtering facepiece respirator (FFR) has been used widely in Thailand. Decontamination methods including ultraviolet C (UVC) germicidal irradiation and 70% alcohol have been implemented to decontaminate these respirators. We then examined the inactivation potential of different decontamination processes on porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) and numerous bacterial strains, most of which were skin-derived. To enable rigorous integrity of the masks after repeated decontamination processes, fit tests by the Bitrex test, tensile strength and elongation at break were also evaluated. Our results showed that UVC irradiation at a dose of 3 J/cm2 can eradicate bacteria after 60 min and viruses after 10 min. No fungi were found on the mask surface before decontamination. The good fit test results, tensile strength and elongation at break were still maintained after multiple cycles of decontamination. No evidence of physical degradation was found by gross visual inspection. Alcohol (70%) is also an easy and effective way to eradicate microorganisms on respirators. As the current pandemic is expected to continue for months to years, the need to supply adequate reserves of personnel protective equipment (PPE) and develop effective PPE reprocessing methods is crucial. Our studies demonstrated that the novel silicone mask can be safely reprocessed and decontaminated for many cycles by UVC irradiation, which will help ameliorate the shortage of important protective devices in the COVID-19 pandemic era.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
"Don, doff, discard" to "don, doff, decontaminate"-FFR and mask integrity and inactivation of a SARS-CoV-2 surrogate and a norovirus following multiple vaporised hydrogen peroxide-, ultraviolet germicidal irradiation-, and dry heat decontaminations.PLoS One. 2021 May 19;16(5):e0251872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251872. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34010337 Free PMC article.
-
Reusability of filtering facepiece respirators after decontamination through drying and germicidal UV irradiation.BMJ Glob Health. 2020 Oct;5(10):e003110. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003110. BMJ Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 33087392 Free PMC article.
-
The new silicone elastometric half-piece respirator, VJR-NMU: A novel and effective tool to prevent COVID-19.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 31;15(12):e0237206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237206. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33382705 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic and personal protective equipment shortage: protective efficacy comparing masks and scientific methods for respirator reuse.Gastrointest Endosc. 2020 Sep;92(3):519-523. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.04.048. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020. PMID: 32353457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Practical Approach to Filtering Facepiece Respirator Decontamination and Reuse: Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation.Curr Treat Options Infect Dis. 2021;13(2):35-46. doi: 10.1007/s40506-021-00247-8. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Curr Treat Options Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33841050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Ultraviolet Type C Radiation in Inactivating Relevant Veterinary Viruses on Experimentally Contaminated Surfaces.Pathogens. 2022 Jun 15;11(6):686. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11060686. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35745540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oral E, Wannomae KK, Connolly R, Gardecki J, Leung HM, Muratoglu O, et al.. Vapor H2O2 sterilization as a decontamination method for the reuse of N95 respirators in the COVID-19 emergency. MedRxiv. 2020. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.11.20062026 - DOI
-
- Bergman MS, Viscusi DJ, Heimbuch BK, Wander JD, Sambol AR, Shaffer RE. Evaluation of multiple (3-Cycle) decontamination processing for filtering facepiece respirators. J Eng Fiber Fabr. 2010;5: 33–41.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Decontamination and Reuse of Filtering Facepiece Respirators. 2020. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/ppe-strategy/decontaminati...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

