Longer term outcomes with single-agent belantamab mafodotin in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: 13-month follow-up from the pivotal DREAMM-2 study
- PMID: 34314018
- PMCID: PMC8597112
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.33809
Longer term outcomes with single-agent belantamab mafodotin in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: 13-month follow-up from the pivotal DREAMM-2 study
Abstract
Background: On the basis of the DREAMM-2 study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03525678), single-agent belantamab mafodotin (belamaf) was approved for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) who received ≥4 prior therapies, including anti-CD38 therapy. The authors investigated longer term efficacy and safety outcomes in DREAMM-2 after 13 months of follow-up among patients who received belamaf 2.5 mg/kg.
Methods: DREAMM-2 is an ongoing, phase 2, open-label, 2-arm study investigating belamaf (2.5 or 3.4 mg/kg) in patients with RRMM who had disease progression after ≥3 lines of therapy and were refractory to immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors and refractory and/or intolerant to an anti-CD38 therapy. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients that achieved an overall response, assessed by an independent review committee.
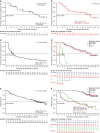
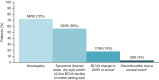
Results: As of January 31, 2020, 10% of patients still received belamaf 2.5 mg/kg. Thirty-one of 97 patients (32%; 97.5% confidence interval [CI], 21.7%-43.6%) achieved an overall response, and 18 responders achieved a very good partial response or better. Median estimated duration of response, overall survival, and progression-free survival were 11.0 months (95% CI, 4.2 months to not reached), 13.7 months (95% CI, 9.9 months to not reached), and 2.8 months (95% CI, 1.6-3.6 months), respectively. Response and survival outcomes in patients who had high-risk cytogenetics or renal impairment were consistent with outcomes in the overall population. Outcomes were poorer in patients with extramedullary disease. In patients who had a clinical response and prolonged dose delays (>63 days; mainly because of corneal events), 88% maintained or deepened responses during their first prolonged dose delay. Overall, there were no new safety signals during this follow-up.
Conclusions: Extended follow-up confirms sustained clinical activity without new safety signals with belamaf in this heavily pretreated patient population with RRMM.
Keywords: B-cell maturation antigen; antibody-drug conjugate; clinical activity; monoclonal antibody; multiple myeloma.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Sagar Lonial reports grant funding and personal fees from Celgene and Takeda and personal fees from Novartis, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Amgen, Merck, and Janssen outside the submitted work. Hans C. Lee reports research funding and personal fees from Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda; personal fees from Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, and Sanofi; and research funding from Daiichi Sankyo and Regeneron outside the submitted work. Ashraf Badros reports consulting fees from Amgen outside the submitted work. Suzanne Trudel reports consulting fees from Celgene, Amgen, and GlaxoSmithKline; honoraria from Celgene, Janssen, Takeda, Sanofi, Karyopharm, and Amgen Canada; and research funding from Celgene, Janssen, Amgen, GlaxoSmithKline, and Genentech outside the submitted work. Ajay K. Nooka reports consulting fees from Amgen, Janssen Oncology, Celgene, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Takeda, Oncopeptides, and Karyopharm Therapeutics; personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline; and research funding from Amgen, Janssen Oncology, and Takeda outside the submitted work. Ajai Chari reports consulting fees from Celgene, Novartis, Amgen, Janssen Oncology, Seattle Genetics, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Genzyme, Oncopeptides, Takeda, Antengene, GlaxoSmithKline, and Secura Bio; and research funding from Celgene, Novartis, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, Amgen, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda outside the submitted work. Natalie Callander reports research funding from Cellectar outside the submitted work. Douglas Sborov reports consulting fees, honoraria, and personal fees from Janssen outside the submitted work. Attaya Suvannasankha reports consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, and Karyopharm Therapeutics; research funding from GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and Celgene; and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline and Janssen outside the submitted work. Katja Weisel reports consulting fees/honoraria from Amgen, Adaptive, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, GlaxoSmithKline, Karyopharm, Takeda and Sanofi; and research funding from Amgen, Celgene, Sanofi, and Janssen outside the submitted work. Peter M. Voorhees reports personal fees from Adaptive Biotechnologies, Bristol‐Myers Squibb/Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Oncopeptides, and TeneoBio outside the submitted work. Linsey Womersley is an employee of GlaxoSmithKline. January Baron, Trisha Piontek, Eric Lewis, and Joanna Opalinska are employees of and hold stock/shares in GlaxoSmithKline. Ira Gupta is an employee of and holds stock/shares in GlaxoSmithKline and Novartis. Adam D. Cohen reports grant funding from GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and Novartis; personal fees from Janssen, Takeda, Oncopeptides, Kite Pharma, Genentech/Roche, AstraZeneca, and Seattle Genetics; and personal fees and other support from GlaxoSmithKline and Celgene outside the submitted work. Al‐Ola Abdallah made no disclosures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-agent belantamab mafodotin in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: Final analysis of the DREAMM-2 trial.Cancer. 2023 Dec 1;129(23):3746-3760. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34987. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37622738 Free PMC article.
-
Belantamab mafodotin for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (DREAMM-2): a two-arm, randomised, open-label, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Feb;21(2):207-221. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30788-0. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31859245 Clinical Trial.
-
DREAMM-2: Indirect Comparisons of Belantamab Mafodotin vs. Selinexor + Dexamethasone and Standard of Care Treatments in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma.Adv Ther. 2021 Nov;38(11):5501-5518. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01884-7. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34561812 Free PMC article.
-
The role of belantamab mafodotin for patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma.Ther Adv Hematol. 2020 Dec 14;11:2040620720979813. doi: 10.1177/2040620720979813. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Hematol. 2020. PMID: 33403093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular Toxicity of Belantamab Mafodotin, an Oncological Perspective of Management in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma.Front Oncol. 2021 May 11;11:678634. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.678634. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34046363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal efficacy and safety modeling and simulation framework to aid dose selection of belantamab mafodotin for patients with multiple myeloma.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;12(10):1411-1424. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13016. Epub 2023 Aug 2. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37465991 Free PMC article.
-
Single-agent belantamab mafodotin in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: Final analysis of the DREAMM-2 trial.Cancer. 2023 Dec 1;129(23):3746-3760. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34987. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37622738 Free PMC article.
-
Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in a Multiple Myeloma Patient After Belantamab Mafodotin Therapy and Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2024 Nov 1;25:e944681. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.944681. Am J Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39482831 Free PMC article.
-
A Phase I First-in-Human Study of ABBV-383, a B-Cell Maturation Antigen × CD3 Bispecific T-Cell Redirecting Antibody, in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma.J Clin Oncol. 2022 Nov 1;40(31):3576-3586. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01504. Epub 2022 Aug 27. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36029527 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dissecting molecular mechanisms of immune microenvironment dysfunction in multiple myeloma and precursor conditions.J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2023;9:17. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2022.110. Epub 2023 May 16. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2023. PMID: 38213954 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

