A Chinese patient with developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEE) carrying a TRPM3 gene mutation: a paediatric case report
- PMID: 34074259
- PMCID: PMC8167971
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-021-02719-8
A Chinese patient with developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEE) carrying a TRPM3 gene mutation: a paediatric case report
Abstract
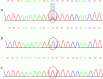
Background: Developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs) are a heterogeneous group of chronic encephalopathies characterized by epilepsy with comorbid intellectual disability that are frequently associated with de novo nonsynonymous coding variants in ion channels, cell-surface receptors, and other neuronally expressed genes. Mutations in TRPM3 were identified as the cause of DEE. We report a novel patient with DEE carrying a de novo missense mutation in TRPM3, p.(S1202T); this missense mutation has never been reported.
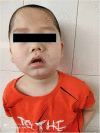
Case presentation: A 7-year and 2-month-old Chinese patient who had recurrent polymorphic seizures was clinically diagnosed with DEE. A de novo missense mutation in TRPM3, which has not yet been reported, was identified in this case. The patient had a clinical phenotype consistent with previous reports.
Conclusions: These findings could expand the spectrum of TRPM3 mutations and might also support that de novo substitutions of TRPM3 are a cause of DEE.
Keywords: Case report; DEE; Seizure; TRPM3; Video-EEG.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that this manuscript has no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
De novo substitutions of TRPM3 cause intellectual disability and epilepsy.Eur J Hum Genet. 2019 Oct;27(10):1611-1618. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0462-x. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31278393 Free PMC article.
-
Gain of channel function and modified gating properties in TRPM3 mutants causing intellectual disability and epilepsy.Elife. 2020 May 19;9:e57190. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57190. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32427099 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodevelopmental disorders caused by variants in TRPM3.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024 Jun;1871(5):119709. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119709. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38522727 Review.
-
Description of a novel patient with the TRPM3 recurrent p.Val837Met variant.Eur J Med Genet. 2021 Nov;64(11):104320. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2021.104320. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Eur J Med Genet. 2021. PMID: 34438093
-
The newest TRP channelopathy: Gain of function TRPM3 mutations cause epilepsy and intellectual disability.Channels (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):386-397. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2021.1908781. Channels (Austin). 2021. PMID: 33853504 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Variants Relate to Fasting Plasma Glucose, 2-Hour Postprandial Glucose, Glycosylated Hemoglobin, and BMI in Prediabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 1;13:778069. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.778069. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35299963 Free PMC article.
-
Gain-of-function variants in the ion channel gene TRPM3 underlie a spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders.Elife. 2023 Jan 17;12:e81032. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81032. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36648066 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologically targeting transient receptor potential channels for seizures and epilepsy: Emerging preclinical evidence of druggability.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Apr;244:108384. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108384. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36933703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial Agonistic Actions of Sex Hormone Steroids on TRPM3 Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 20;22(24):13652. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413652. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948452 Free PMC article.
-
De novo TRPM3 missense variant associated with neurodevelopmental delay and manifestations of cerebral palsy.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2024 Jan 10;9(4):a006293. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a006293. Print 2023 Dec. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2024. PMID: 37684057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nilius B. TRP channels in disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1772;2007:805–812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

