Integrating genomics and metabolomics for scalable non-ribosomal peptide discovery
- PMID: 34050176
- PMCID: PMC8163882
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23502-4
Integrating genomics and metabolomics for scalable non-ribosomal peptide discovery
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Integrating genomics and metabolomics for scalable non-ribosomal peptide discovery.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 8;12(1):4318. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24441-w. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34238936 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
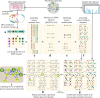
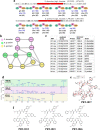
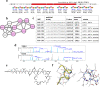
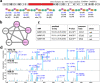
Non-Ribosomal Peptides (NRPs) represent a biomedically important class of natural products that include a multitude of antibiotics and other clinically used drugs. NRPs are not directly encoded in the genome but are instead produced by metabolic pathways encoded by biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs). Since the existing genome mining tools predict many putative NRPs synthesized by a given BGC, it remains unclear which of these putative NRPs are correct and how to identify post-assembly modifications of amino acids in these NRPs in a blind mode, without knowing which modifications exist in the sample. To address this challenge, here we report NRPminer, a modification-tolerant tool for NRP discovery from large (meta)genomic and mass spectrometry datasets. We show that NRPminer is able to identify many NRPs from different environments, including four previously unreported NRP families from soil-associated microbes and NRPs from human microbiota. Furthermore, in this work we demonstrate the anti-parasitic activities and the structure of two of these NRP families using direct bioactivity screening and nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry, illustrating the power of NRPminer for discovering bioactive NRPs.
Conflict of interest statement
P.A.P. is a co-founder, has an equity interest and receives income from Digital Proteomics, LLC. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. B.B. and H.M. are co-founders and have equity interests from Chemia.ai, LLC. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
NRPquest: Coupling Mass Spectrometry and Genome Mining for Nonribosomal Peptide Discovery.J Nat Prod. 2014 Aug 22;77(8):1902-9. doi: 10.1021/np500370c. Epub 2014 Aug 12. J Nat Prod. 2014. PMID: 25116163 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-based cryptic gene discovery and functional identification of NRPS siderophore peptide in Streptomyces peucetius.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;97(3):1213-22. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4268-9. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22825833
-
Bioactive compounds synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases and type-I polyketide synthases discovered through genome-mining and metagenomics.Biotechnol Lett. 2012 Aug;34(8):1393-403. doi: 10.1007/s10529-012-0919-2. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Biotechnol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22481301 Review.
-
A genome-wide analysis of nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene clusters and their peptides in a Planktothrix rubescens strain.BMC Genomics. 2009 Aug 25;10:396. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-396. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19706155 Free PMC article.
-
Toolbox for Antibiotics Discovery from Microorganisms.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016 Sep;349(9):683-91. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201600064. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016. PMID: 27311607 Review.
Cited by
-
Nerpa: A Tool for Discovering Biosynthetic Gene Clusters of Bacterial Nonribosomal Peptides.Metabolites. 2021 Oct 11;11(10):693. doi: 10.3390/metabo11100693. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34677408 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Metabolomic-Genomic Workflows Accelerate Microbial Natural Product Discovery.Anal Chem. 2022 Sep 6;94(35):11959-11966. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02245. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35994737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A metabologenomics strategy for rapid discovery of polyketides derived from modular polyketide synthases.Chem Sci. 2024 Nov 4;16(4):1696-1706. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04174g. eCollection 2025 Jan 22. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39568943 Free PMC article.
-
Precision enzyme discovery through targeted mining of metagenomic data.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024 Jan 11;14(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s13659-023-00426-8. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024. PMID: 38200389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Microbiome-Derived Solutions and Methodologies Are Founding a New Era in Skin Health and Care.Pathogens. 2022 Jan 20;11(2):121. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020121. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215065 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016;79:629–661. - PubMed
-
- Li JWH, Vederas JC. Drug discovery and natural products: end of an era or an endless frontier? Science. 2009;325:161–165. - PubMed
-
- Harvey AL, Edrada-Ebel R, Quinn RJ. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015;14:111–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

