Which are the most sensitive search filters to identify randomized controlled trials in MEDLINE?
- PMID: 33013212
- PMCID: PMC7524635
- DOI: 10.5195/jmla.2020.912
Which are the most sensitive search filters to identify randomized controlled trials in MEDLINE?
Abstract
Objective: The Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews contains search filters to find randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in Ovid MEDLINE: one maximizing sensitivity and another balancing sensitivity and precision. These filters were originally published in 1994 and were adapted and updated in 2008. To determine the performance of these filters, the authors tested them and thirty-six other MEDLINE filters against a large new gold standard set of relevant records.
Methods: We identified a gold standard set of RCT reports published in 2016 from the Cochrane CENTRAL database of controlled clinical trials. We retrieved the records in Ovid MEDLINE and combined these with each RCT filter. We calculated their sensitivity, relative precision, and f-scores.
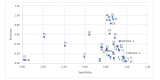
Results: The gold standard comprised 27,617 records. MEDLINE searches were run on July 16, 2019. The most sensitive RCT filter was Duggan et al. (sensitivity=0.99). The Cochrane sensitivity-maximizing RCT filter had a sensitivity of 0.96 but was more precise than Duggan et al. (0.14 compared to 0.04 for Duggan). The most precise RCT filters had 0.97 relative precision and 0.83 sensitivity.
Conclusions: The Cochrane Ovid MEDLINE sensitivity-maximizing RCT filter can continue to be used by Cochrane reviewers and to populate CENTRAL, as it has very high sensitivity and a slightly better precision relative to more sensitive filters. The results of this study, which used a very large gold standard to compare the performance of all known RCT filters, allows searchers to make better informed decisions about which filters to use for their work.
Copyright © 2020 Julie Glanville, Eleanor Kotas, Robin Featherstone, Gordon Dooley.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Search strategies to identify diagnostic accuracy studies in MEDLINE and EMBASE.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 11;2013(9):MR000022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000022.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24022476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Search strategies to identify observational studies in MEDLINE and Embase.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 12;3(3):MR000041. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000041.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30860595 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the performance of methodological search filters to improve the efficiency of evidence information retrieval: five literature reviews and a qualitative study.Health Technol Assess. 2017 Nov;21(69):1-148. doi: 10.3310/hta21690. Health Technol Assess. 2017. PMID: 29188764 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological developments in searching for studies for systematic reviews: past, present and future?Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 25;2:78. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-2-78. Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24066664 Free PMC article.
-
Search strategies (filters) to identify systematic reviews in MEDLINE and Embase.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Sep 8;9(9):MR000054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000054.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37681507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hydroxychloroquine for Non-Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023 Apr 7;120(4):e20220380. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220380. eCollection 2023. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37042856 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
Development and evaluation of a search filter to identify prognostic factor studies in Ovid MEDLINE.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022 Apr 10;22(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12874-022-01595-9. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022. PMID: 35399050 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic optic neuropathy management: a systematic review.Eye (Lond). 2024 Aug;38(12):2312-2318. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-03129-7. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Eye (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38862644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Results publications are inadequately linked to trial registrations: An automated pipeline and evaluation of German university medical centers.Clin Trials. 2022 Jun;19(3):337-346. doi: 10.1177/17407745221087456. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Clin Trials. 2022. PMID: 35362331 Free PMC article.
-
Translation and validation of PubMed and Embase search filters for identification of systematic reviews, intervention studies, and observational studies in the field of first aid.J Med Libr Assoc. 2021 Oct 1;109(4):599-608. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2021.1219. J Med Libr Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34858089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, eds. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. Cochrane; 2011. [updated March 2011].
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research Quality. Methods guide for effectiveness and comparative effectiveness reviews Rockville, MD: The Agency; 2014. - PubMed
-
- Committee on Standards for Systematic Reviews of Comparative Effectiveness Research; Institute of Medicine. Finding what works in health care: standards for systematic reviews Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre C, Glanville J, Beale S, Boachie C, Duffy S, Fraser C, Harbour J, McCool R, Smith L. Assessing the performance of methodological search filters to improve the efficiency of evidence information retrieval: five literature reviews and a qualitative study. Health Technol Assess. November;21(69):1–148. DOI: 10.3310/hta21690. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources