(-)-Catechin-7- O-β-d-Apiofuranoside Inhibits Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by Suppressing the STAT3 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 31861943
- PMCID: PMC7017110
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9010030
(-)-Catechin-7- O-β-d-Apiofuranoside Inhibits Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by Suppressing the STAT3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
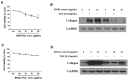
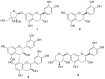
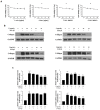
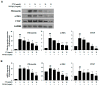
Hepatic fibrosis is characterized by the abnormal deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. During hepatic fibrogenesis, hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation followed by chronic injuries is considered a key event in fibrogenesis, and activated HSCs are known to comprise approximately 90% of ECM-producing myofibroblasts. Here, we demonstrated that (-)-catechin-7-O-β-d-apiofuranoside (C7A) significantly inhibited HSC activation via blocking the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway. This is the first study to show the hepatic protective effects of C7A with possible mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. In our bioactivity screening, we figured out that the EtOH extract of Ulmusdavidiana var. japonica root barks, which have been used as a Korean traditional medicine, inhibited collagen synthesis in HSCs. Four catechins isolated from the EtOAc fraction of the EtOH extract were compared with each other in terms of reduction in collagen, which is considered as a marker of hepatic protective effects, and C7A showed the strongest inhibitory effects on HSC activation in protein and qPCR analyses. As a possible mechanism, we investigated the effects of C7A on the STAT3 signaling pathway, which is known to activate HSCs. We found that C7A inhibited phosphorylation of STAT3 and translocation of STAT3 to nucleus. C7A also inhibited expressions of MMP-2 and MMP-9, which are downstream genes of STAT3 signaling. Anti-fibrotic effects of C7A were evaluated in a thioacetamide (TAA)-induced liver fibrosis model, which indicated that C7A significantly inhibited ECM deposition through inhibiting STAT3 signaling. C7A decreased serum levels of aspartate amino transferase and alanine transaminase, which were markedly increased by TAA injection. Moreover, ECM-associated proteins and mRNA expression were strongly suppressed by C7A. Our study provides the experimental evidence that C7A has inhibitory effects on HSC activation after live injury and has preventive and therapeutic potentials for the management of hepatic fibrosis.
Keywords: (–)-Catechin-7-O-β-d-apiofuranoside; STAT3; Ulmus davidiana var. japonica; hepatic fibrosis; hepatic stellate cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective Potency of Chrysophanol 8-O-Glucoside from Rheum palmatum L. against Hepatic Fibrosis via Regulation of the STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 27;21(23):9044. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239044. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33261209 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Oridonin Analog CYD0682 Inhibits Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via the Heat Shock Protein 90-Dependent STAT3 Pathway.J Surg Res. 2024 Jun;298:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2023.12.056. Epub 2024 Mar 26. J Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38537450
-
Interleukin-10 induces senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells via STAT3-p53 pathway to attenuate liver fibrosis.Cell Signal. 2020 Feb;66:109445. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109445. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 31730896
-
Hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic functions of interleukin-22: therapeutic potential for the treatment of alcoholic liver disease.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Aug;28 Suppl 1(0 1):56-60. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12032. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23855297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extra- and Intra-Cellular Mechanisms of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 14;9(8):1014. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081014. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440218 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic potential and pathogenic performance of circulating miR-146b, miR-194, and miR-214 in liver fibrosis.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Jun 26;8(4):471-480. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.06.004. eCollection 2023 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 37434946 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Potency of Chrysophanol 8-O-Glucoside from Rheum palmatum L. against Hepatic Fibrosis via Regulation of the STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 27;21(23):9044. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239044. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33261209 Free PMC article.
-
Ulmus parvifolia Modulates Platelet Functions and Inhibits Thrombus Formation by Regulating Integrin αIIbβ3 and cAMP Signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 19;11:698. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00698. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32508642 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics counteract the expression of hepatic profibrotic genes via the attenuation of TGF-β/SMAD signaling and autophagy in hepatic stellate cells.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 20;17(1):e0262767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262767. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35051234 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in the effect of ferroptosis of HSCs on the development of liver fibrosis.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Sep 26;10:1258870. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1258870. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37860583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2018R1A2B2006879/National Research Foundation of Korea/International
- NRF-2012M3A9C4048775/National Research Foundation of Korea/International
- 20000105, Development of Cosmeceutical Material Platform using Organo-Nano Complexes based on Natural Active Compounds/Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

