A comparison of metrics and performance characteristics of different search strategies for article retrieval for a systematic review of the global epidemiology of kidney and urinary diseases
- PMID: 30340535
- PMCID: PMC6194627
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-018-0569-8
A comparison of metrics and performance characteristics of different search strategies for article retrieval for a systematic review of the global epidemiology of kidney and urinary diseases
Abstract
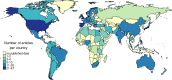
Background: Conducting a systematic review requires a comprehensive bibliographic search. Comparing different search strategies is essential for choosing those that cover all useful data sources. Our aim was to develop search strategies for article retrieval for a systematic review of the global epidemiology of kidney and urinary diseases, and evaluate their metrics and performance characteristics that could be useful for other systematic epidemiologic reviews.
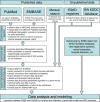
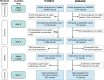
Methods: We described the methodological framework and analysed approaches applied in the previously conducted systematic review intended to obtain published data for global estimates of the kidney and urinary disease burden. We used several search strategies in PubMed and EMBASE, and compared several metrics: number needed to retrieve (NNR), number of extracted data rows, number of covered countries, and when appropriate, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and accuracy.
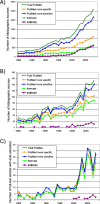
Results: The initial search obtained 29,460 records from PubMed, and 4247 from EMBASE. After the revision, the full text of 381 and 14 articles respectively was obtained for data extraction (the percentage of useful records is 1.3% for PubMed, 0.3% for EMBASE). For PubMed we developed two search strategies and compared them with a 'gold standard' formed by merging their results: free word search strategy (FreeWoSS) was based on the search for keywords in all fields, and subject headings based search strategy (SuHeSS) used only MeSH-mapped conditions and countries names. SuHeSS excluded almost 15% of useful articles and data rows extracted from them, but had a lower NNR of 40 and higher specificity. FreeWoSS had better sensitivity and was able to cover the vast majority of articles and extracted data rows, but had a higher NNR of 65.
Conclusions: The sensitive FreeWoSS strategy provides more data for modelling, while the more specific SuHeSS strategy could be used when resources are limited. EMBASE has limited value for our systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Search strategies to identify diagnostic accuracy studies in MEDLINE and EMBASE.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 11;2013(9):MR000022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000022.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24022476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a search filter to identify equity-focused studies: reducing the number needed to screen.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018 Oct 12;18(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0567-x. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018. PMID: 30314471 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
High-performance information search filters for CKD content in PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and EMBASE.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Jan;65(1):26-32. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25059221
-
Optimal database combinations for literature searches in systematic reviews: a prospective exploratory study.Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 6;6(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13643-017-0644-y. Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29208034 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Search strategies (filters) to identify systematic reviews in MEDLINE and Embase.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Sep 8;9(9):MR000054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000054.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37681507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.Lancet. 2020 Feb 29;395(10225):709-733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32061315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095–2128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2163–2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CJL M, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2197–2223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

