Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Diagnosis and Treatment Update
- PMID: 29280746
- PMCID: PMC5790328
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.2017.S007
Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Diagnosis and Treatment Update
Abstract
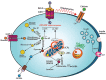
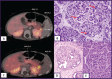
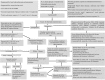
Pancreatic β-cells are finely tuned to secrete insulin so that plasma glucose levels are maintained within a narrow physiological range (3.5-5.5 mmol/L). Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia (HH) is the inappropriate secretion of insulin in the presence of low plasma glucose levels and leads to severe and persistent hypoglycaemia in neonates and children. Mutations in 12 different key genes (ABCC8, KCNJ11, GLUD1, GCK, HADH, SLC16A1, UCP2, HNF4A, HNF1A, HK1, PGM1 and PMM2) that are involved in the regulation of insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells have been described to be responsible for the underlying molecular mechanisms leading to congenital HH. In HH due to the inhibitory effect of insulin on lipolysis and ketogenesis there is suppressed ketone body formation in the presence of hypoglycaemia thus leading to increased risk of hypoglycaemic brain injury. Therefore, a prompt diagnosis and immediate management of HH is essential to avoid hypoglycaemic brain injury and long-term neurological complications in children. Advances in molecular genetics, imaging techniques (18F-DOPA positron emission tomography/computed tomography scanning), medical therapy and surgical advances (laparoscopic and open pancreatectomy) have changed the management and improved the outcome of patients with HH. This review article provides an overview to the background, clinical presentation, diagnosis, molecular genetics and therapy in children with different forms of HH.
Keywords: Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia; children; congenital hyperinsulinaemia; diffuse congenital hyperinsulinism; focal congenital hyperinsulinism sirolimus..
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnosis and treatment of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia and its implications for paediatric endocrinology.Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017;2017:9. doi: 10.1186/s13633-017-0048-8. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28855921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis and management of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Aug;32(4):551-573. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30086874 Review.
-
Congenital hyperinsulinism: recent updates on molecular mechanisms, diagnosis and management.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Sep 21;35(3):279-296. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2021-0369. Print 2022 Mar 28. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34547194 Review.
-
The Diagnosis and Management of Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;7(2):86-97. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.1891. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26316429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia: genetic mechanisms, diagnosis and management.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2012 Jul;35(4):589-601. doi: 10.1007/s10545-011-9441-2. Epub 2012 Jan 10. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2012. PMID: 22231386 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoglycemia due to PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway defects: two novel cases and review of the literature.Hormones (Athens). 2021 Dec;20(4):623-640. doi: 10.1007/s42000-021-00287-1. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Hormones (Athens). 2021. PMID: 33876391 Review.
-
Referrals for Hypoglycemia to the Pediatric Endocrine Clinic: Is It For Real?Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2018 Nov;57(13):1588-1591. doi: 10.1177/0009922818793342. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2018. PMID: 30198308 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Early diagnosis of focal congenital hyperinsulinism: A fluorine-18-labeled l-dihydroxyphenylalanine positron emission tomography/computed tomography study.World J Nucl Med. 2021 Nov 1;20(4):395-397. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.wjnm_159_20. eCollection 2021 Oct-Dec. World J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 35018160 Free PMC article.
-
Families' Experiences of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Management of Congenital Hyperinsulinism: A Thematic Analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 19;13:894559. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.894559. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35928891 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Transporters, Channelopathies, and Glucose Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 27;20(10):2590. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102590. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31137773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hussain K, Aynsley-Green A. Hyperinsulinism in infancy: understanding the pathophysiology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35:1312–1317. - PubMed
-
- Gutgold A, Gutgold DJ, Glaser B, Szalat A. Diagnosis of ABCC8 Congenital Hyperinsulinism of Infancy in a 20-Year-Old Man Evaluated for Factitious Hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:345–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
