Novel NR2F1 variants likely disrupt DNA binding: molecular modeling in two cases, review of published cases, genotype-phenotype correlation, and phenotypic expansion of the Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome
- PMID: 28963436
- PMCID: PMC5701304
- DOI: 10.1101/mcs.a002162
Novel NR2F1 variants likely disrupt DNA binding: molecular modeling in two cases, review of published cases, genotype-phenotype correlation, and phenotypic expansion of the Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome
Abstract
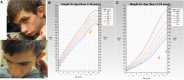
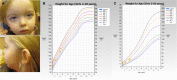
Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome (BBSOAS) is a recently described autosomal dominant disorder caused by mutations in the NR2F1 gene. There are presently 28 cases of BBSOAS described in the literature. Its common features include developmental delay, intellectual disability, hypotonia, optic nerve atrophy, attention deficit disorder, autism spectrum disorder, seizures, hearing defects, spasticity, and thinning of the corpus callosum. Here we report two unrelated probands with novel, de novo, missense variants in NR2F1 The first is a 14-yr-old male patient with hypotonia, intellectual disability, optic nerve hypoplasia, delayed bone age, short stature, and altered neurotransmitter levels on cerebrospinal fluid testing. The second is a 5-yr-old female with severe developmental delay, motor and speech delay, and repetitive motion behavior. Whole-exome sequencing identified a novel missense NR2F1 variant in each case, Cys86Phe in the DNA-binding domain in Case 1, and a Leu372Pro in the ligand-binding domain in Case 2. The presence of clinical findings compatible with BBSOAS along with structural analysis at atomic resolution using homology-based molecular modeling and molecular dynamic simulations, support the pathogenicity of these variants for BBSOAS. Short stature, abnormal CNS neurotransmitters, and macrocephaly have not been previously reported for this syndrome and may represent a phenotypic expansion of BBSOAS. A review of published cases along with new evidence from this report support genotype-phenotype correlations for this disorder.
Keywords: amblyopia; aplasia/hypoplasia of the optic nerve; cortical visual impairment; decreased CSF homovanillic acid (HVA); microretrognathia; optic disc hypoplasia; oromotor apraxia; relative macrocephaly; severe muscular hypotonia; short stature.
© 2017 Kaiwar et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel dominant-negative NR2F1 frameshift mutation and a phenotypic expansion of the Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome.Eur J Med Genet. 2020 Oct;63(10):104019. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2020.104019. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Eur J Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32712214
-
Phenotypic expansion of Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome and further evidence for genotype-phenotype correlations.Am J Med Genet A. 2020 Jun;182(6):1426-1437. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61580. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Am J Med Genet A. 2020. PMID: 32275123
-
The expanding clinical phenotype of Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome: 20 new cases and possible genotype-phenotype correlations.Genet Med. 2016 Nov;18(11):1143-1150. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.18. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Genet Med. 2016. PMID: 26986877
-
Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf Optic Atrophy Syndrome Presenting as New-Onset Psychosis in a 32-Year-Old Man: A Case Report and Literature Review.J Psychiatr Pract. 2020 Jan;26(1):58-62. doi: 10.1097/PRA.0000000000000440. J Psychiatr Pract. 2020. PMID: 31913971 Review.
-
Pathophysiological Heterogeneity of the BBSOA Neurodevelopmental Syndrome.Cells. 2022 Apr 8;11(8):1260. doi: 10.3390/cells11081260. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NR2F1 regulates regional progenitor dynamics in the mouse neocortex and cortical gyrification in BBSOAS patients.EMBO J. 2020 Jul 1;39(13):e104163. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019104163. Epub 2020 Jun 2. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32484994 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding variants alter GATA2 expression in rhombomere 4 motor neurons and cause dominant hereditary congenital facial paresis.Nat Genet. 2023 Jul;55(7):1149-1163. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01424-9. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Nat Genet. 2023. PMID: 37386251 Free PMC article.
-
14th EUNOS Congress: PORTO, PORTUGAL, 16-19 JUNE 2019.Neuroophthalmology. 2019 Jun 7;43(Suppl 1):1-221. doi: 10.1080/01658107.2019.1608780. eCollection 2019 Jun. Neuroophthalmology. 2019. PMID: 31528195 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Novel NR2F1 variant identified by whole-exome sequencing in a patient with Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Jul;70(7):2762-2764. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1061_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35791240 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Aspects of the Neurodevelopmental Gene NR2F1: From Animal Models to Human Pathology.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Dec 15;14:767965. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.767965. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34975398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Kateb H, Shimony JS, Vineyard M, Manwaring L, Kulkarni S, Shinawi M. 2013. NR2F1 haploinsufficiency is associated with optic atrophy, dysmorphism and global developmental delay. Am J Med Genet A 161A: 377–381. - PubMed
-
- Armentano M, Chou SJ, Tomassy GS, Leingärtner A, O'Leary DD, Studer M. 2007. COUP-TFI regulates the balance of cortical patterning between frontal/motor and sensory areas. Nat Neurosci 10: 1277–1286. - PubMed
-
- BIOVIA. 2017. Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA, Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, Release 2017. Dassault Systèmes, San Diego.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
