Anti-obesity effects of Yerba Mate (Ilex Paraguariensis): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 26408319
- PMCID: PMC4583719
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-015-0859-1
Anti-obesity effects of Yerba Mate (Ilex Paraguariensis): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a major health problem. A food field research that has recently aroused considerable interest is the potential of natural products to counteract obesity. Yerba Mate may be helpful in reducing body weight and fat. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of Yerba Mate supplementation in Korean subjects with obesity.
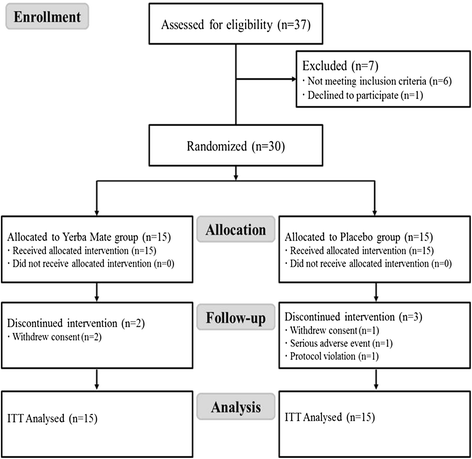
Methods: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted. Subjects with obesity (body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 but < 35 kg/m(2) and waist-hip ratio (WHR) ≥ 0.90 for men and ≥ 0.85 for women) were given oral supplements of Yerba Mate capsules (n = 15) or placebos (n = 15) for 12 weeks. Subjects take three capsules per each meal, total three times in a day (3 g/day). Measured outcomes were efficacy (abdominal fat distribution, anthropometric parameters and blood lipid profiles) and safety (adverse events, laboratory test results and vital signs).
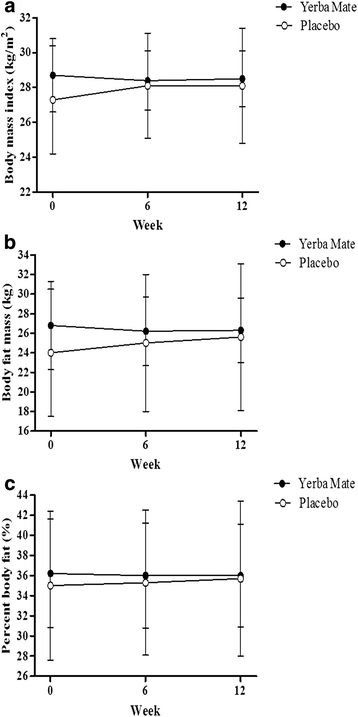
Results: During 12 weeks of Yerba Mate supplementation, decreases in body fat mass (P = 0.036) and percent body fat (P = 0.030) compared to the placebo group were statistically significant. WHR was significantly decreased (P = 0.004) in the Yerba Mate group compared to the placebo group. No clinically significant changes in any safety parameters were observed.
Conclusions: Yerba Mate supplementation decreased body fat mass, percent body fat and WHR. Yerba Mate was a potent anti-obesity reagent that did not produce significant adverse effects. These results suggested that Yerba Mate supplementation may be effective for treating obese individuals.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: (NCT01778257).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiobesity effects of yerba maté extract (Ilex paraguariensis) in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009 Dec;17(12):2127-33. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.158. Epub 2009 May 14. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009. PMID: 19444227
-
Yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis) improves microcirculation of volunteers with high blood viscosity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Exp Gerontol. 2015 Feb;62:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2014.12.016. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Exp Gerontol. 2015. PMID: 25562195 Clinical Trial.
-
The positive effects of yerba maté (Ilex paraguariensis) in obesity.Nutrients. 2015 Jan 22;7(2):730-50. doi: 10.3390/nu7020730. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 25621503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Dietary Supplementation with Yerba Mate Ameliorates Diet-Induced Obesity and Metabolic Disorders in Mice by Regulating Energy Expenditure and Lipid Metabolism.J Med Food. 2017 Dec;20(12):1168-1175. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2017.3995. Epub 2017 Sep 5. J Med Food. 2017. PMID: 28872427
-
Yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) for new therapeutic and nutraceutical interventions: A review of patents issued in the last 20 years (2000-2020).Phytother Res. 2023 Feb;37(2):527-548. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7632. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 36180970 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Citrus depressa Hayata juice on high-fat diet-induced obesity in HBV transgenic mice.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 10;10(2):e24438. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24438. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312542 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review on clinically proven medicinal plants in the treatment of overweight and obesity, with mechanistic insights.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 4;9(2):e13493. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13493. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36816319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of yerba mate and green tea on paraoxonase and leptin levels in patients affected by overweight or obesity and dyslipidemia: a randomized clinical trial.Nutr J. 2019 Jan 19;18(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12937-018-0426-y. Nutr J. 2019. PMID: 30660196 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Health Benefits of Bioactive Compounds from the Genus Ilex, a Source of Traditional Caffeinated Beverages.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 5;10(11):1682. doi: 10.3390/nu10111682. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30400635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Products to Counteract the Epidemic of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorders.Molecules. 2016 Jun 22;21(6):807. doi: 10.3390/molecules21060807. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27338339 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO/IASO/IOTF . The asia-pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Melbourne, Australia: Health Communications Australia; 2000.
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet No 311. 2015. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

