Vitamin C treatment attenuates hemorrhagic shock related multi-organ injuries through the induction of heme oxygenase-1
- PMID: 25387896
- PMCID: PMC4246491
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-442
Vitamin C treatment attenuates hemorrhagic shock related multi-organ injuries through the induction of heme oxygenase-1
Abstract
Background: Vitamin C (VitC) has recently been shown to exert beneficial effects, including protecting organ function and inhibiting inflammation, in various critical care conditions, but the specific mechanism remains unclear. Induction of heme oxygenase (HO)-1, a heat shock protein, has been shown to prevent organ injuries in hemorrhagic shock (HS) but the relationship between VitC and HO-1 are still ill-defined so far. Here we conducted a systemic in vivo study to investigate if VitC promoted HO-1 expression in multiple organs, and then tested if the HO-1 induction property of VitC was related to its organ protection and anti-inflammatory effect.
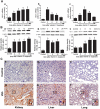
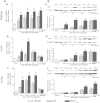
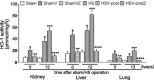
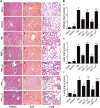
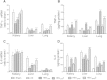
Methods: Firstly, to determine the HO-1 induction property of VitC, the HO-1 level were measured in tissues including kidney, liver and lung of the normal and HS model of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats after VitC treatment (100 mg/kg body weight). Secondly, to testify if VitC prevented HS related organ injuries via inducing HO-1, the HS model of rats were separately pre- and post-treated with VitC, and some of them also received Zinc protoporphyrin (Znpp), a specific HO-1 inhibitor. The HO-1 activity in tissues was tested; the organ injuries (as judged by histological changes in tissues and the biochemical indicators level in serum) and inflammatory response in tissues (as judged by the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines Tumor necrosis factor-α and Interleukin-6 ) were analyzed.
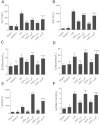
Results: The HO-1 mRNA and protein level in kidney, liver, and lung were highly induced by VitC treatement under normal and HS conditions. The HO-1 activity in tissues was enhanced by both VitC pre- and post-treatment, which was shown to improve the organ injuries and inhibit the inflammatory response in the HS model of rats. Of note, the beneficial effects of VitC were abolished after HO-1 activity was blocked by Znpp.
Conclusions: VitC led to a profound induction of HO-1 in multiple organs including the kidney, liver and lung, and this property might be responsible for the organ protection and inflammation inhibitory effects of both pre- and post-treatment with VitC in HS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammation and Edema in the Lung and Kidney of Hemorrhagic Shock Rats Are Alleviated by Biliary Tract External Drainage via the Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway.Inflammation. 2015 Dec;38(6):2242-51. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0208-z. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 26253294
-
Pharmacological preconditioning with vitamin C attenuates intestinal injury via the induction of heme oxygenase-1 after hemorrhagic shock in rats.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 13;9(6):e99134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099134. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24927128 Free PMC article.
-
Hemin arginate-induced heme oxygenase 1 expression improves liver microcirculation and mediates an anti-inflammatory cytokine response after hemorrhagic shock.Shock. 2008 May;29(5):583-90. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318157e526. Shock. 2008. PMID: 18414232
-
[Heat shock response in a rat model of septic multiple organ dysfunction syndrome].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999 Nov;114(5):295-302. doi: 10.1254/fpj.114.295. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10621943 Review. Japanese.
-
Vitamin C to Improve Organ Dysfunction in Cardiac Surgery Patients-Review and Pragmatic Approach.Nutrients. 2018 Jul 27;10(8):974. doi: 10.3390/nu10080974. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30060468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation and Edema in the Lung and Kidney of Hemorrhagic Shock Rats Are Alleviated by Biliary Tract External Drainage via the Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway.Inflammation. 2015 Dec;38(6):2242-51. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0208-z. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 26253294
-
Vitamin C Attenuates Hemorrhagic Shock-induced Dendritic Cell-specific Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 3-grabbing Nonintegrin Expression in Tubular Epithelial Cells and Renal Injury in Rats.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Jul 20;129(14):1731-6. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.185868. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 27411463 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of heme oxygenase-1 recombinant Lactococcus lactis on the intestinal barrier of hemorrhagic shock rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017 Jun 5;50(7):e5601. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20175601. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017. PMID: 28591377 Free PMC article.
-
Intensive management of severe acute pancreatitis.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Nov;7(22):687. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.10.58. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31930088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-dose vitamin C alleviates pancreatic injury via the NRF2/NQO1/HO-1 pathway in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jul;8(14):852. doi: 10.21037/atm-19-4552. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32793696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minei JP, Cuschieri J, Sperry J, Moore EE, West MA, Harbrecht BG, O’Keefe GE, Cohen MJ, Moldawer LL, Tompkins RG, Maier RV. The changing pattern and implications of multiple organ failure after blunt injury with hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med. 2012;40:1129–1135. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182376e9f. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shibahara S. Regulation of heme oxygenase gene expression. Semin Hematol. 1988;25:370–376. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/14/442/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

