Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism
- PMID: 25363760
- PMCID: PMC4402723
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13772
Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism
Abstract
The genetic architecture of autism spectrum disorder involves the interplay of common and rare variants and their impact on hundreds of genes. Using exome sequencing, here we show that analysis of rare coding variation in 3,871 autism cases and 9,937 ancestry-matched or parental controls implicates 22 autosomal genes at a false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05, plus a set of 107 autosomal genes strongly enriched for those likely to affect risk (FDR < 0.30). These 107 genes, which show unusual evolutionary constraint against mutations, incur de novo loss-of-function mutations in over 5% of autistic subjects. Many of the genes implicated encode proteins for synaptic formation, transcriptional regulation and chromatin-remodelling pathways. These include voltage-gated ion channels regulating the propagation of action potentials, pacemaking and excitability-transcription coupling, as well as histone-modifying enzymes and chromatin remodellers-most prominently those that mediate post-translational lysine methylation/demethylation modifications of histones.
Figures
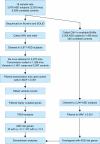
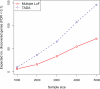


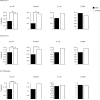

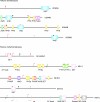

Similar articles
-
The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder.Nature. 2014 Nov 13;515(7526):216-21. doi: 10.1038/nature13908. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25363768 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent Mutations of Chromatin-Remodeling Genes and Kinase Receptors in Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 May 1;22(9):2301-10. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1841. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26700204 Free PMC article.
-
Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma.Nature. 2012 Jan 29;482(7384):226-31. doi: 10.1038/nature10833. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22286061
-
Recent progresses in molecular genetics of autism spectrum disorders.Yi Chuan. 2015 Sep;37(9):845-54. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.15-281. Yi Chuan. 2015. PMID: 26399524 Review.
-
From the genetic architecture to synaptic plasticity in autism spectrum disorder.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015 Sep;16(9):551-63. doi: 10.1038/nrn3992. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26289574 Review.
Cited by
-
BCL11A intellectual developmental disorder: defining the clinical spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlations.Eur J Hum Genet. 2025 Mar;33(3):312-324. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01701-z. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Eur J Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 39448799
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Neurological Disorders.Subcell Biochem. 2021;97:411-436. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-67171-6_16. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33779926
-
DECO: a framework for jointly analyzing de novo and rare case/control variants, and biological pathways.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbab067. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab067. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33791774 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Verbal Scores in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Retrospective Trial.Cureus. 2024 Jan 4;16(1):e51654. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51654. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38318543 Free PMC article.
-
NRSF/REST lies at the intersection between epigenetic regulation, miRNA-mediated gene control and neurodevelopmental pathways associated with Intellectual disability (ID) and Schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 10;12(1):438. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02199-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36216811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ronald A, Hoekstra RA. Autism spectrum disorders and autistic traits: a decade of new twin studies. American journal of medical genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric genetics : the official publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2011;156B:255–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01MH100233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH095034/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L010305/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P30 HD015052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS073601/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT091310/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01MH100239/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH083565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD055751/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH089208/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094400/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH100233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH083565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2MH089952/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH089208/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH095034/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097849/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH100229/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 091986/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0500870/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH061009/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089952/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH100209/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH100239/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01MH100209/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01MH100229/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH095797/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD15052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH089482/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH089482/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

