Postanalytical tools improve performance of newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 24875301
- PMCID: PMC4262759
- DOI: 10.1038/gim.2014.62
Postanalytical tools improve performance of newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare performance metrics of postanalytical interpretive tools of the Region 4 Stork collaborative project to the actual outcome based on cutoff values for amino acids and acylcarnitines selected by the California newborn screening program.
Methods: This study was a retrospective review of the outcome of 176,186 subjects born in California between 1 January and 30 June 2012. Raw data were uploaded to the Region 4 Stork Web portal as .csv files to calculate tool scores for 48 conditions simultaneously using a previously unpublished functionality, the tool runner. Scores for individual target conditions were deemed informative when equal or greater to the value representing the first percentile rank of known true-positive cases (17,099 cases in total).
Results: In the study period, the actual false-positive rate and positive predictive value were 0.26 and 10%, respectively. Utilization of the Region 4 Stork tools, simple interpretation rules, and second-tier tests could have achieved a false-positive rate as low as 0.02% and a positive predictive value >50% by replacing the cutoff system with Region 4 Stork tools as the primary method for postanalytical interpretation.
Conclusion: Region 4 Stork interpretive tools, second-tier tests, and other evidence-based interpretation rules could have reduced false-positive cases by up to 90% in California.
Figures

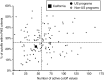
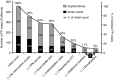
Similar articles
-
Enhanced interpretation of newborn screening results without analyte cutoff values.Genet Med. 2012 Jul;14(7):648-55. doi: 10.1038/gim.2012.2. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Genet Med. 2012. PMID: 22766634
-
[Newborn screening program and blood amino acid profiling in early neonates with citrin deficiency].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Oct 2;57(10):797-801. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2019.10.014. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31594068 Chinese.
-
Effects of birth weight on profiles of dried blood amino-acids and acylcarnitines.Ann Clin Biochem. 2018 Jan;55(1):92-99. doi: 10.1177/0004563216688038. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Ann Clin Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29064274
-
Application of mass spectrometry in newborn screening: about both small molecular diseases and lysosomal storage diseases.Top Curr Chem. 2014;336:177-96. doi: 10.1007/128_2012_354. Top Curr Chem. 2014. PMID: 22911488 Review.
-
Tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening for inborn errors of intermediary metabolism: abnormal profile interpretation.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(26):4511-22. doi: 10.2174/092986712803251539. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22934775 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Approach to Improve Newborn Screening for Congenital Hypothyroidism by Integrating Covariate-Adjusted Results of Different Tests into CLIR Customized Interpretive Tools.Int J Neonatal Screen. 2021 Apr 23;7(2):23. doi: 10.3390/ijns7020023. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2021. PMID: 33922835 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Maternal Age and Blood Markers for Metabolic Disease in Newborns.Metabolites. 2023 Dec 20;14(1):5. doi: 10.3390/metabo14010005. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38276295 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal metabolomics in dried bloodspots yields profiles informing newborn screening for succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency.JIMD Rep. 2020 Feb 26;53(1):29-38. doi: 10.1002/jmd2.12075. eCollection 2020 May. JIMD Rep. 2020. PMID: 32395407 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Whole Genome and Exome Sequencing for Newborn Screening: Challenges and Opportunities for Population Health.Front Pediatr. 2021 Jul 19;9:663752. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.663752. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34350142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Butyrylcarnitine Elevation in Newborn Screening: Reducing False Positives and Distinguishing between Two Rare Diseases through the Evaluation of New Ratios.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 7;11(12):3247. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123247. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137468 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McHugh D, Cameron CA, Abdenur JE, et al. Clinical validation of cutoff target ranges in newborn screening of metabolic disorders by tandem mass spectrometry: a worldwide collaborative project. Genet Med. 2011;13:230–254. - PubMed
-
- Watson MS, Mann MY, Lloyd-Puryear MA, Rinaldo P, Howell RR. Newborn screening: toward a uniform screening panel and system [executive summary] Genet Med. 2006;8 suppl:1S–11S. - PubMed
-
- Marquardt G, Currier R, McHugh DM, et al. Enhanced interpretation of newborn screening results without analyte cutoff values. Genet Med. 2012;14:648–655. - PubMed
-
- Merritt JL, 2nd, Vedal S, Abdenur JE, et al. Infants suspected to have very-long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency from newborn screening. Mol Genet Metab. 2014;111:484–492. - PubMed
-
- Rinaldo P, Zafari S, Tortorelli S, Matern D. Making the case for objective performance metrics in newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006;12:255–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

